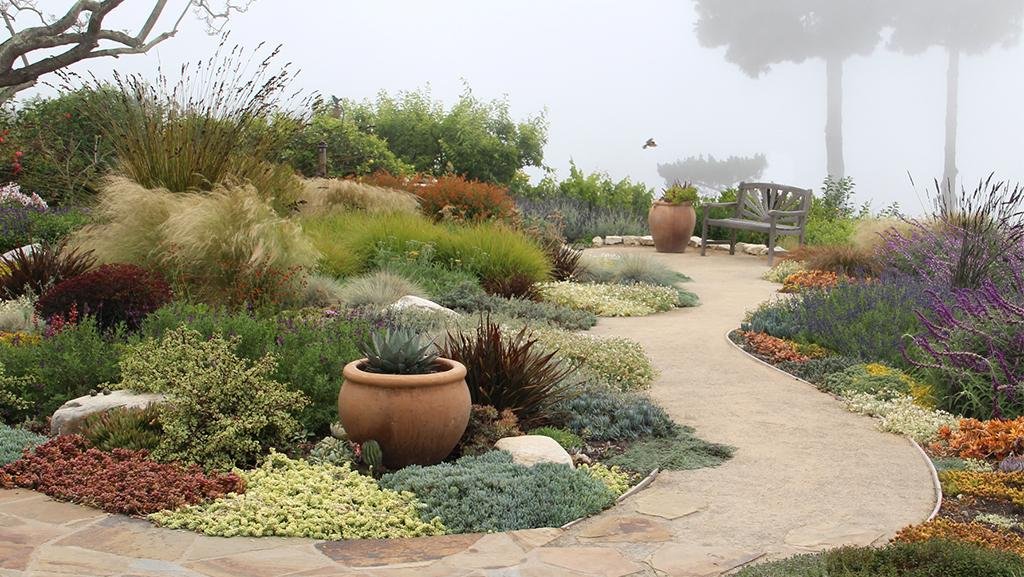
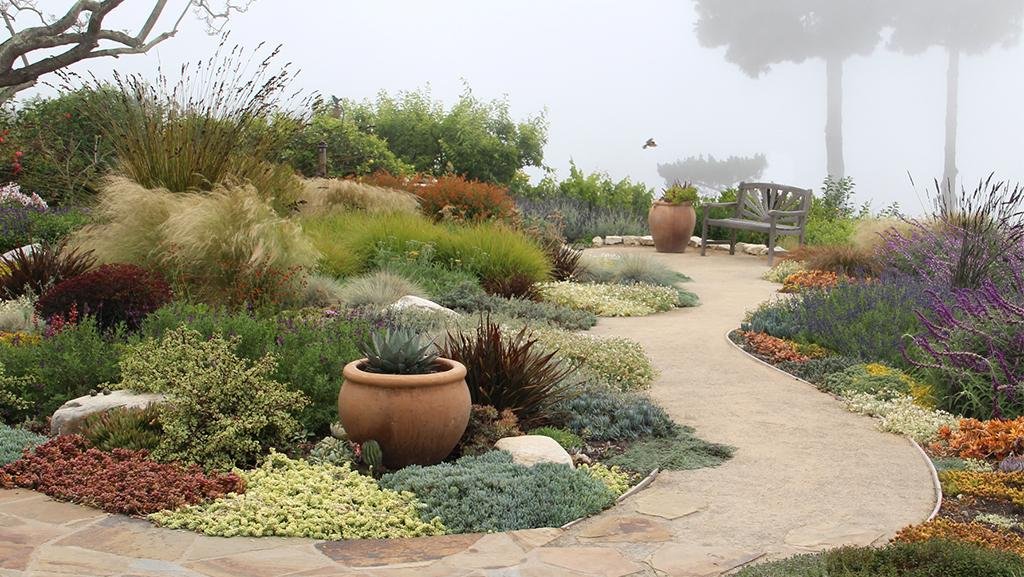
Imagine transforming your dry, barren yard into an oasis of lush greenery and beautiful blooms, all while conserving water and reducing maintenance. This is the power of xeriscaping, a sustainable landscaping technique specifically designed for hot climates. By strategically selecting drought-resistant plants, creating efficient irrigation systems, and implementing smart design principles, xeriscaping allows you to create an aesthetically pleasing and environmentally friendly outdoor space that thrives in even the hottest conditions. Discover the secrets of xeriscaping and unlock the potential of your landscape.

This image is property of www.monrovia.com.
1. What is Xeriscaping?
1.1 Definition
Xeriscaping, also known as water-wise or drought-resistant landscaping, is a sustainable landscaping approach that focuses on creating beautiful and functional outdoor spaces while minimizing water usage. The term “xeriscape” is derived from the Greek word “xeros,” meaning dry, and “scape,” referring to a landscape. By incorporating water-efficient techniques and using drought-tolerant plants, xeriscaping promotes responsible water usage and helps conserve this valuable resource.
1.2 Origins
The concept of xeriscaping originated in arid regions such as Arizona and New Mexico, where water scarcity and drought conditions posed significant challenges for traditional landscaping practices. As a means of addressing these issues, xeriscaping emerged as a practical and environmentally-friendly landscaping solution. It has since gained popularity in hot climates worldwide, offering a sustainable and aesthetically pleasing alternative to water-thirsty lawns and high maintenance gardens.
1.3 Benefits
Xeriscaping offers numerous benefits for homeowners and communities in hot climates. Firstly, it significantly reduces water consumption by up to 50-75% compared to conventional landscapes. By using drought-tolerant plants and implementing water conservation techniques, xeriscaping helps to minimize water waste and preserve this precious resource, particularly in regions prone to droughts. Additionally, xeriscaping requires significantly less maintenance, saving homeowners time and reducing the need for expensive irrigation systems and lawn care services. Moreover, xeriscaped landscapes can enhance the aesthetic appeal of outdoor spaces, creating visually appealing and ecologically balanced environments that attract wildlife and provide a sense of tranquility.
2. Planning Xeriscaping in Hot Climates
2.1 Assessing the Climate
Before embarking on a xeriscaping project in a hot climate, it is crucial to assess the specific climate conditions of the area. Factors such as average annual rainfall, temperature fluctuations, and the duration and intensity of dry periods must be considered. This information will guide the selection of appropriate plants and help determine the most effective water conservation techniques for the landscape.
2.2 Creating a Landscape Design Plan
A well-thought-out design plan is essential for successful xeriscaping in hot climates. Consider factors such as the layout of the outdoor space, existing structures, and the desired functionality of different areas. Determine focal points, pathways, and zones for various activities, such as outdoor dining or relaxation areas. This plan will serve as a visual guide during the implementation stage and ensure the creation of a cohesive and functional xeriscape design.
2.3 Choosing Suitable Plants
One of the key elements of xeriscaping in hot climates is the selection of drought-tolerant plants that can thrive in arid conditions. Native plants are always a great choice as they are naturally adapted to the local climate and require minimal water once established. Additionally, consider adapted plant species from similar regions with comparable climatic conditions. These plants have evolved to survive in hot and dry environments and can bring color, texture, and biodiversity to the xeriscape. Be sure to research plant water requirements and group them based on their water needs, ensuring efficient use of irrigation water.
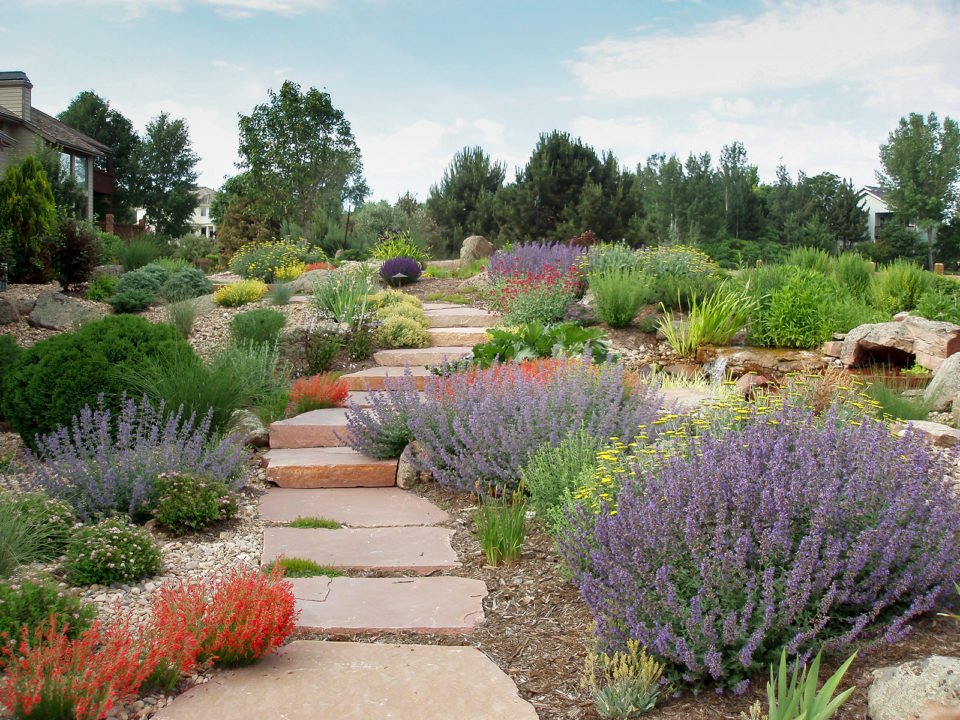

This image is property of cdn.5280.com.
3. Water Conservation Techniques
3.1 Soil Preparation and Improvement
Proper soil preparation and improvement are essential for xeriscaping success in hot climates. To improve water retention and drainage, incorporate organic matter such as compost into the soil. This enhances soil structure, allowing it to retain moisture for longer periods and preventing water runoff. Amending the soil with organic matter also improves its ability to absorb water, reducing the need for frequent irrigation.
3.2 Proper Irrigation Systems
Selecting the right irrigation systems is crucial for efficient water usage in xeriscaping. Drip irrigation is particularly effective for delivering water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing evaporation and ensuring that water reaches its intended destination. Additionally, consider using weather-based irrigation controllers that adjust watering schedules based on real-time weather data. This prevents overwatering during periods of rainfall and reduces water usage during cooler seasons.
3.3 Mulching and Composting
Mulching plays a vital role in water conservation by reducing soil evaporation and inhibiting weed growth. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or bark, around plants and on open soil areas. Mulch also helps control soil temperature, preventing excessive heating during hot summers. Composting organic waste can also contribute to water conservation by improving soil health and moisture retention. The nutrients from compost promote plant growth and reduce the need for excessive watering.
4. Incorporating Drought-Tolerant Plants
4.1 Native Plants
Native plants are a cornerstone of xeriscaping in hot climates. These plants have evolved to thrive in the local environment and are naturally adapted to the regional climate. They require less water, have lower maintenance needs, and provide habitat and food sources for local wildlife. Incorporating native plants in a xeriscape design not only enhances the sustainability and ecological value of the landscape but also creates a sense of harmony with the surrounding natural environment.
4.2 Adapted Plant Species
In addition to native plants, consider incorporating adapted plant species from other regions with similar climatic conditions. These plants have proven their ability to withstand heat, drought, and other challenging environmental factors. By researching and selecting adapted plant species, you can diversify the plant palette of your xeriscape and introduce unique colors, textures, and forms to create a visually appealing landscape.
4.3 Grouping Plants based on Water Needs
Efficient water management is a key aspect of xeriscaping. Grouping plants with similar water needs allows for targeted irrigation and ensures that each plant receives the appropriate amount of water. By segregating plants based on their water requirements, it is possible to avoid overwatering or underwatering, leading to healthier and more resilient plants. Consider the plant’s natural habitat and adapt their placement in the landscape to meet their specific watering needs.

This image is property of www.phgmag.com.
5. Efficient Watering Strategies
5.1 Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient watering strategy for xeriscaping in hot climates. It involves the use of porous hoses or pipes that deliver water directly to the plant’s root zone. This method minimizes water loss due to evaporation and prevents water runoff. Additionally, drip irrigation allows for precise control over the amount of water delivered to each plant, reducing the risk of overwatering and ensuring efficient water usage.
5.2 Rainwater Harvesting
In regions with intermittent rainfall, rainwater harvesting can supplement irrigation water and minimize reliance on traditional water sources. Collect rainwater from roofs and other surfaces, directing it to storage tanks or underground cisterns. This harvested water can be used for landscape irrigation, reducing the demand for treated water and promoting sustainable water usage.
5.3 Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers are technologically advanced devices that use real-time weather data to adjust watering schedules automatically. They consider factors such as rainfall, temperature, and soil moisture levels to optimize irrigation schedules and prevent water waste. By installing a smart irrigation system, you can ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right time, even in hot climates where water conservation is crucial.
6. Designing Hardscapes for Water Efficiency
6.1 Choosing Permeable Materials
When designing hardscapes, such as patios, walkways, or driveways, choose permeable materials whenever possible. Permeable materials, such as gravel, permeable pavers, or mulch, allow water to infiltrate the soil rather than creating runoff. This helps replenish groundwater supplies and reduces the burden on storm drainage systems. Additionally, permeable materials can help prevent heat buildup, keeping outdoor areas cooler during hot weather.
6.2 Creating Shade Structures
In hot climates, providing shade is essential for creating comfortable outdoor spaces. Incorporate shade structures, such as pergolas, arbor, or shade sails, into your xeriscape design. These structures not only provide relief from the sun’s intense rays but also minimize water evaporation from the surrounding soil. By strategically positioning shade structures, you can create shaded areas that promote outdoor activities while reducing water loss.
6.3 Implementing Rain Gardens
Rain gardens are attractive and functional features that help manage stormwater runoff while providing habitat for beneficial wildlife. Determine low-lying areas in the landscape where excess water tends to accumulate during heavy rains and transform them into rain gardens. Plant a variety of native and adapted plant species in these areas, as they can help absorb and filter excess water, reduce erosion, and recharge groundwater supplies.

This image is property of d3i6fh83elv35t.cloudfront.net.
7. Proper Maintenance Tips
7.1 Pruning and Trimming Techniques
Regular pruning and trimming are essential to keep xeriscaped landscapes looking neat and well-maintained. Remove dead or damaged plant material to maintain the health of the plants and promote proper airflow. Prune branches that may be obstructing walkways or interfering with other plants. Proper pruning and trimming techniques promote plant growth, enhance the appearance of the landscape, and prevent the spread of diseases.
7.2 Weed Control
Weeds can compete with xeriscape plants for water and nutrients, particularly in hot climates where resources are scarce. Implement effective weed control measures to prevent weed growth and ensure that water is used efficiently. Use organic weed control methods, such as mulching or hand weeding, to avoid the use of harmful chemicals that can negatively impact the environment and the health of the xeriscape.
7.3 Seasonal Adjustments
Make seasonal adjustments to your xeriscape maintenance routine to accommodate changing weather conditions. During extremely hot periods, increase watering frequency or adjust irrigation schedules to prevent plant stress. In cooler months, reduce watering to avoid overwatering and promote plant resilience. Regularly monitor the condition of plants and adjust maintenance practices accordingly to keep your xeriscape thriving throughout the year.
8. Xeriscaping Success Stories in Hot Climates
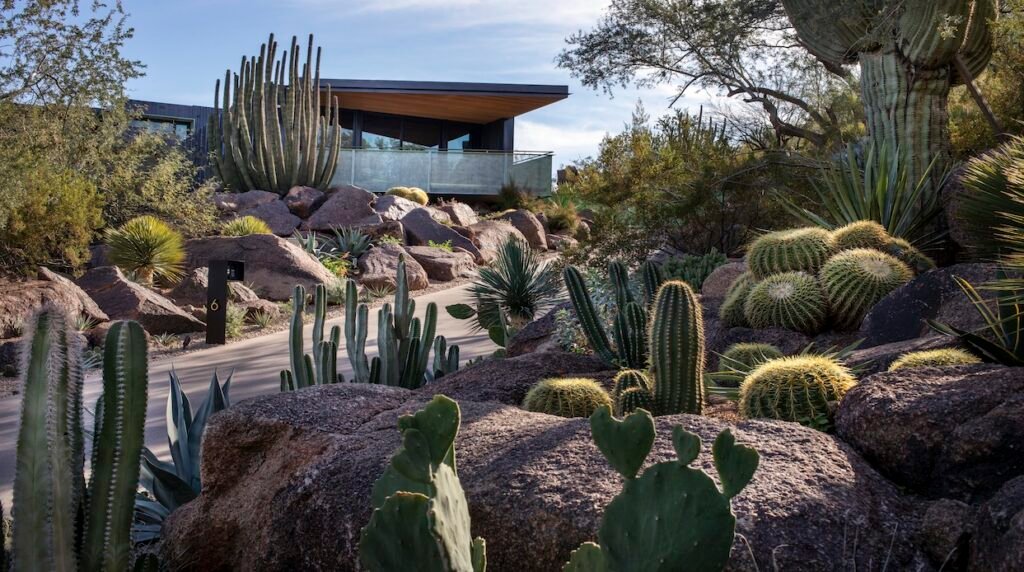
8.1 Case Study 1: Desert Botanical Garden in Phoenix, Arizona
The Desert Botanical Garden in Phoenix, Arizona, is an excellent example of successful xeriscaping in a hot climate. This renowned garden showcases the diversity and beauty of desert plants, featuring a stunning array of cacti, succulents, and other drought-tolerant species. With its commitment to water conservation, the garden demonstrates how xeriscaping can create an inspiring and environmentally-responsible outdoor space in an arid region.
8.2 Case Study 2: Denver Water Xeriscape Demo Garden in Denver, Colorado
The Denver Water Xeriscape Demo Garden in Denver, Colorado, showcases the possibilities of xeriscaping in a hot and semi-arid climate. This educational garden provides visitors with practical examples of water-efficient landscaping techniques and drought-tolerant plant choices. By highlighting the benefits and beauty of xeriscaping, the garden encourages homeowners and communities to embrace sustainable landscaping practices.
8.3 Case Study 3: Sydney Olympic Park in Sydney, Australia
The Sydney Olympic Park in Sydney, Australia, is another remarkable example of xeriscaping in a hot climate. With a focus on water conservation and environmental stewardship, the park incorporates drought-tolerant plants and innovative water management strategies. By utilizing rainwater harvesting, efficient irrigation systems, and native plantings, the park demonstrates how xeriscaping can create sustainable and visually striking landscapes.

This image is property of www.gardeningchannel.com.
9. Overcoming Challenges in Xeriscaping for Hot Climates
9.1 Soil Condition Issues
Hot climates often present challenges related to soil conditions, such as poor drainage, compacted soil, or nutrient deficiencies. Address these issues by amending the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve soil structure and fertility. Implementing proper soil preparation techniques and regular soil testing can help overcome soil condition challenges and create an optimal growing environment for xeriscape plants.
9.2 Pest and Disease Management
Pests and diseases can pose challenges in xeriscaping, especially in hot climates where plants may be more vulnerable to stress. Implement integrated pest management techniques, such as planting pest-resistant species, encouraging natural predators, and practicing good sanitation. Regularly monitor plants for signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate action to prevent their spread. Proper plant selection, soil improvement, and ongoing maintenance can help minimize pest and disease issues in xeriscapes.
9.3 Practical Constraints
Xeriscaping in hot climates may face practical constraints such as limited water availability, municipal regulations, or homeowner association restrictions. Overcoming these challenges requires creative problem-solving and adaptive strategies. Consider installing rainwater harvesting systems or utilizing greywater for irrigation. Work within the framework of local regulations and engage with community organizations to promote the benefits and importance of xeriscaping. With open communication and a proactive approach, it is possible to navigate these constraints and create a thriving xeriscape.
10. Conclusion
Xeriscaping offers a sustainable and visually appealing landscaping solution for hot climates. By incorporating water conservation techniques, selecting drought-tolerant plants, and implementing efficient watering strategies, homeowners can create beautiful outdoor spaces that are both environmentally friendly and cost-effective. Xeriscaping success stories around the world demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in overcoming the challenges of water scarcity and extreme temperatures. With proper planning, maintenance, and a commitment to responsible water usage, xeriscaping can transform hot climate landscapes into vibrant, resilient, and sustainable environments.