Welcome! In this article, we will be discussing the importance of ecological preservation, specifically zero emissions and biodiversity conservation. We’ll explore how these practices contribute to a healthier planet and the well-being of both human and animal species. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of why it is essential to reduce emissions and protect biodiversity, and how each of us can make a positive impact in preserving our environment. So, let’s get started and discover the significance of eco-friendly practices!

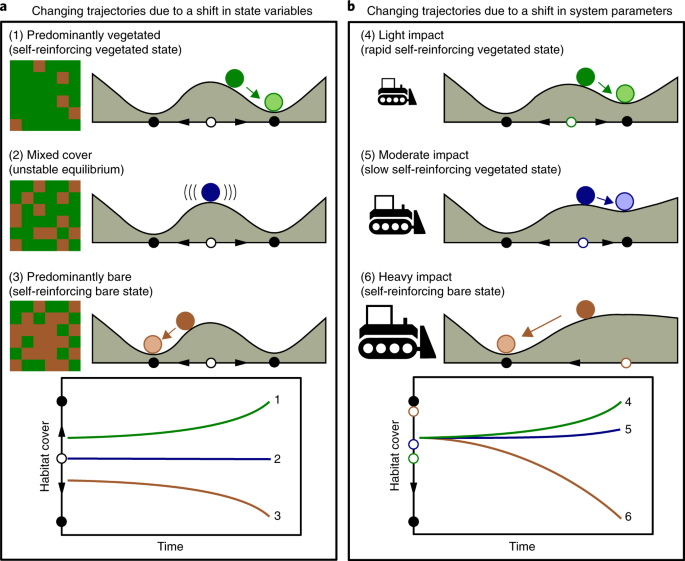
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Overview of Ecological Preservation
Ecological preservation plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems. It involves the conservation and protection of natural resources, habitats, and biodiversity to ensure the sustainability of our environment for future generations. This article will explore the importance of ecological preservation and its connection to zero emissions and biodiversity conservation.
Importance of Ecological Preservation
Ecological preservation is of paramount importance due to the numerous benefits it provides. First and foremost, it helps to maintain the health and stability of ecosystems. By preserving natural habitats and protecting biodiversity, we ensure the functioning of intricate ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, water purification, and pollination. These processes are essential for the survival of both plant and animal species.
Moreover, ecological preservation also contributes to climate regulation. Healthy ecosystems act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas responsible for climate change. By protecting forests, wetlands, and other natural areas, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and promote global environmental stability.
Definition of Ecological Preservation
Ecological preservation refers to the conscious efforts made by individuals, communities, and organizations to protect and conserve the natural environment. It involves adopting sustainable practices, minimizing environmental impacts, and promoting the responsible use of resources. Ecological preservation encompasses actions such as reducing pollution, conserving energy, preserving biodiversity, and implementing renewable energy technologies.
Effects of Failure to Preserve Ecological Balance
Failure to preserve ecological balance can have severe consequences for both the environment and human well-being. When ecosystems are disrupted or destroyed, it can lead to the loss of biodiversity, habitat degradation, and the disruption of ecological processes. This can result in the extinction of species, the spread of invasive species, and the collapse of ecosystems.
Furthermore, the degradation of ecosystems can also directly impact human populations. When natural resources such as water, food, and clean air become scarce or polluted, it can have detrimental effects on human health and livelihoods. Additionally, the loss of ecosystem services, such as the provision of clean water, can have economic implications for communities and nations.
Zero Emissions as a Key Strategy
To effectively address the challenges of ecological preservation, transitioning to zero emissions practices is crucial. Zero emissions refers to the concept of minimizing or eliminating the release of greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. This can be achieved through various strategies, including renewable energy adoption, energy efficiency improvements, and the implementation of sustainable transportation systems.
Understanding Zero Emissions
Zero emissions does not imply that all activities will cease to emit greenhouse gases. It recognizes that some sectors, such as agriculture and waste management, may continue to release certain amounts of greenhouse gases. However, the goal is to offset these emissions through the implementation of carbon sequestration measures and the use of renewable energy sources.
Benefits of Zero Emissions
The adoption of zero emissions practices offers numerous benefits for both the environment and society. First and foremost, it helps to mitigate climate change by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This, in turn, helps to limit the extent of global warming, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events.
Furthermore, zero emissions practices promote sustainable development by reducing reliance on finite fossil fuel resources. By embracing renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, societies can achieve energy independence and promote the growth of clean and green industries.
Transitioning to Zero Emissions Practices
Transitioning to zero emissions practices requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals. Governments can play a vital role by implementing policies and regulations that incentivize the adoption of renewable energy, promote energy efficiency, and support research and development in green technologies.
Businesses can contribute by incorporating sustainable practices into their operations, such as investing in renewable energy generation, improving energy efficiency, and reducing waste. Additionally, individuals can make a difference by embracing sustainable lifestyles, such as reducing energy consumption, using public transportation, and engaging in recycling and composting.

This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Role of Renewable Energy in Zero Emissions
Renewable energy sources play a crucial role in achieving zero emissions and promoting ecological preservation. They provide sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, which are a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to renewable energy technologies, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and promote environmental sustainability.
Overview of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass energy. These sources harness the natural processes of the Earth, such as sunlight, wind, and water flow, to generate clean and renewable energy. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources do not emit greenhouse gases during their operation, making them a sustainable and environmentally friendly choice.
Advantages of Renewable Energy
There are numerous advantages to using renewable energy sources. Firstly, they contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, thus mitigating climate change. Renewable energy is also abundant and widely available, providing a long-term and sustainable solution to meet our energy needs.
Renewable energy technologies also offer economic benefits. They support the growth of green industries, creating job opportunities and driving economic development. Additionally, renewable energy can enhance energy security by reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Implementing Renewable Energy Technologies
The implementation of renewable energy technologies requires a comprehensive approach that includes policy support, financial incentives, and technological advancements. Governments can play a crucial role by establishing favorable regulatory frameworks and providing financial incentives for renewable energy projects.
Businesses can contribute by investing in renewable energy infrastructure and integrating renewable energy solutions into their operations. This can involve installing solar panels, wind turbines, or investing in biomass energy projects. Furthermore, research and development efforts are essential to improve the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy technologies.
Industrial Practices for Zero Emissions
Industrial practices play a significant role in achieving zero emissions and promoting ecological preservation. The adoption of green technologies and sustainable supply chains can help businesses reduce their environmental footprint and minimize their impact on ecosystems.
Green Technologies in Manufacturing
Green technologies, also known as eco-friendly or clean technologies, encompass a wide range of practices and innovations that minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. These technologies include energy-efficient machinery, waste reduction techniques, and water conservation measures.
By implementing green technologies, industries can reduce energy and resource consumption, reduce pollution, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to both ecological preservation and economic sustainability.
Sustainable Supply Chains
Sustainable supply chains aim to minimize the environmental impact associated with the production and transportation of goods. This involves adopting practices such as sustainable sourcing, recyclable packaging, and efficient logistics management.
By implementing sustainable supply chains, businesses can reduce their carbon footprint, promote responsible resource management, and minimize waste generation throughout the entire production and distribution process.
Circular Economy and Zero Waste
The concept of a circular economy emphasizes the importance of reducing, reusing, and recycling resources to minimize waste generation. It aims to move away from the traditional linear model of production and consumption, where resources are extracted, used, and disposed of.
By transitioning to a circular economy, businesses can reduce their reliance on finite resources, minimize waste generation, and promote the efficient use of materials. This contributes to zero emissions by minimizing resource extraction and reducing pollution from waste disposal.

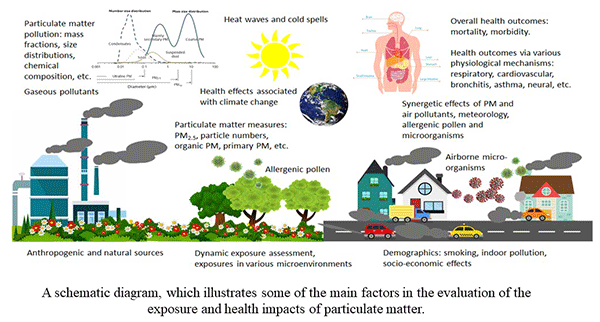
This image is property of insideclimatenews.org.
Biodiversity Conservation and Its Significance
Biodiversity conservation is closely linked to ecological preservation and plays a fundamental role in ensuring the long-term health and resilience of our planet. Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the ecosystems they inhabit.
Definition of Biodiversity
Biodiversity encompasses the variety of species, genetic diversity within species, and the variety of ecosystems on Earth. It is a measure of the richness and uniqueness of life in different habitats and provides the foundation for the functioning of ecosystems.
Importance of Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity conservation is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to maintain the stability and resilience of ecosystems. Each species plays a unique role in the regulation of ecological processes, and the loss of even a single species can have far-reaching consequences. Biodiversity also enhances ecosystem productivity, as different species contribute to nutrient cycling and the provision of ecosystem services.
Additionally, biodiversity conservation is essential for the discovery and development of new medicines, as many pharmaceuticals are derived from natural sources. Moreover, biodiversity has intrinsic value in and of itself, as each species has a right to exist and fulfill its role in the web of life.
Threats to Biodiversity
Biodiversity faces numerous threats, primarily driven by human activities. Habitat destruction, fragmentation, and degradation are widespread issues, with deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion being major contributors. These activities destroy the natural habitats of countless plant and animal species, leading to their decline and extinction.
Furthermore, pollution, overexploitation of resources, invasive species, and climate change also pose significant threats to biodiversity. These factors can disrupt ecological processes and jeopardize the survival of many species.
Conservation Strategies and Initiatives
To address the challenges of biodiversity loss, various conservation strategies and initiatives have been implemented worldwide. These efforts aim to protect and restore habitats, preserve endangered species, and promote sustainable practices.
Protected Areas and National Parks
Protected areas, such as national parks, nature reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries, are crucial for biodiversity conservation. These areas provide habitats for species and serve as refuges for endangered and threatened plants and animals. They also contribute to the restoration of degraded ecosystems and the preservation of genetic diversity.
Protected areas are established and managed by governments and conservation organizations, with the aim of balancing the needs of biodiversity conservation and human activities. These areas provide opportunities for research, education, and eco-tourism, contributing to both ecological preservation and local economies.
Species Conservation Programs
Species conservation programs focus on the protection and recovery of threatened and endangered species. These initiatives involve habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, monitoring and research efforts, and public awareness campaigns.
By targeting specific species, conservation programs aim to prevent their extinction and promote their recovery. These programs often involve collaboration between governments, NGOs, and local communities to ensure the preservation of biodiversity.
Preserving Critical Habitats
Preserving critical habitats is essential for the conservation of biodiversity, as many species rely on specific habitats for their survival. These habitats can include wetlands, coral reefs, old-growth forests, and grasslands, among others.
Preserving critical habitats involves implementing measures such as land acquisition, restoration, and management. It also requires the establishment of protected areas and the enforcement of regulations to prevent habitat destruction and degradation.
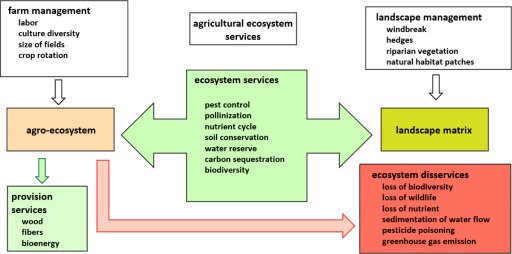
This image is property of ars.els-cdn.com.
International Agreements for Biodiversity Conservation
International agreements play a crucial role in promoting biodiversity conservation and ecological preservation at a global scale. These agreements provide a framework for cooperation among nations and set goals and targets to address biodiversity loss.
Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is an international treaty that aims to promote biodiversity conservation, sustainable use of natural resources, and equitable sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources. It sets out obligations for signatory countries to develop and implement strategies for biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
The CBD encourages the establishment of protected areas, the integration of biodiversity considerations into national decision-making processes, and the promotion of sustainable practices in various sectors.
Aichi Biodiversity Targets
The Aichi Biodiversity Targets were adopted as part of the CBD’s Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020. These targets provide a roadmap for global biodiversity conservation efforts and address key issues such as habitat loss, species extinction, sustainable resource management, and the equitable sharing of benefits from biodiversity.
The Aichi Biodiversity Targets have set ambitious goals to be achieved by 2020, including the conservation of at least 17% of terrestrial and inland water areas and 10% of coastal and marine areas as protected areas.
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) also encompass biodiversity conservation as one of the crucial components for achieving sustainable development. Goal 15 specifically focuses on protecting, restoring, and promoting sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainable forest management, and combatting desertification.
The SDGs provide a comprehensive framework for addressing environmental issues, including biodiversity conservation, while also encompassing social and economic aspects of sustainable development.
Community Involvement in Biodiversity Conservation
Community involvement is vital for the success of biodiversity conservation efforts. Local communities are often the stewards of natural resources and have valuable knowledge and practices that can contribute to ecological preservation.
Engaging Local Communities
Engaging local communities in biodiversity conservation involves actively involving them in decision-making processes, management practices, and sustainable resource use. This can be achieved through the establishment of community-based conservation programs, participatory approaches, and the recognition of indigenous rights and traditional knowledge.
By involving local communities, biodiversity conservation initiatives can benefit from their expertise, ensure the sustainability of conservation efforts, and foster a sense of ownership and stewardship over natural resources.
Indigenous Knowledge and Conservation
Indigenous communities have a deep connection to their ancestral lands and possess unique knowledge and practices that have contributed to biodiversity conservation for generations. Recognizing and respecting indigenous rights and traditional knowledge is essential for the preservation of biodiversity.
Indigenous knowledge often includes detailed observations and understanding of ecosystems, sustainable resource management practices, and traditional conservation practices. Incorporating this knowledge into conservation strategies can enhance the effectiveness and cultural relevance of biodiversity conservation efforts.
Volunteer and Citizen Science Programs
Volunteer and citizen science programs provide opportunities for individuals to contribute to biodiversity conservation efforts. These programs engage the public in data collection, research, and monitoring activities.
By involving volunteers and citizen scientists, conservation initiatives can benefit from a large and diverse workforce, while also raising public awareness about biodiversity conservation. These programs also facilitate the dissemination of scientific knowledge and promote environmental education and stewardship among participants.
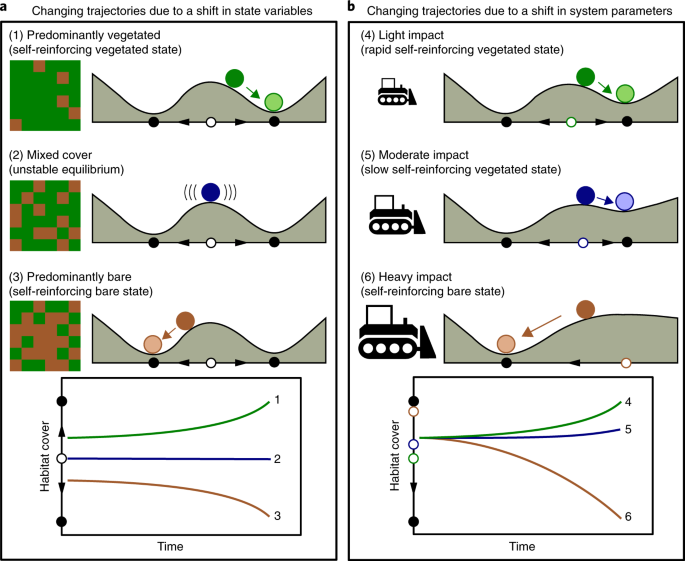
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Economic Benefits of Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity conservation not only contributes to the preservation of ecosystems but also generates economic benefits. The concept of ecosystem services recognizes the multitude of benefits that ecosystems provide to human populations.
Ecosystem Services and their Value
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from healthy ecosystems. These services include the provision of clean air and water, regulation of climate, pollination of crops, nutrient cycling, and the provision of food and raw materials, among others.
The economic value of ecosystem services is often underestimated or overlooked but plays a crucial role in sustaining human well-being and economic activities. Valuing and incorporating ecosystem services into decision-making processes can help to ensure their preservation and promote sustainable development.
Sustainable Tourism and Biodiversity
Biodiversity conservation can also contribute to sustainable tourism, which has become an important economic sector globally. Many tourists are drawn to destinations because of their natural beauty and unique biodiversity.
Sustainable tourism practices involve minimizing the negative environmental impacts associated with tourism activities, promoting cultural awareness and respect, and supporting local economies and communities. By incorporating biodiversity conservation into tourism planning and management, destinations can attract visitors while ensuring the long-term preservation of natural resources.
Green Jobs and Sustainable Development
Biodiversity conservation also presents opportunities for green job creation and sustainable development. Green jobs refer to employment opportunities that contribute to environmental protection, resource efficiency, and the development of clean technologies.
Conservation projects, ecotourism initiatives, environmental education and awareness programs, and sustainable agriculture practices are just a few examples of green jobs that can be created through biodiversity conservation efforts. These jobs not only provide employment but also contribute to the preservation of ecosystems and the promotion of sustainable practices.
Challenges in Ecological Preservation
Several challenges hinder the progress of ecological preservation, making it necessary to address these obstacles to achieve sustainable development.
Balancing Economic Growth and Environmental Protection
One of the main challenges in ecological preservation is finding a balance between economic growth and environmental protection. Often, economic activities, such as industrialization and urbanization, are driven by the exploitation of natural resources, leading to habitat destruction and environmental degradation.
Addressing this challenge requires the adoption of sustainable development practices that integrate environmental considerations into economic decision-making. This involves implementing regulations, incentives, and market mechanisms that promote sustainable resource management and environmentally responsible business practices.
Political and Corporate Commitment
Political and corporate commitment is fundamental for the success of ecological preservation efforts. Governments need to prioritize environmental protection and enact policies and regulations that promote sustainable practices.
Similarly, businesses have a vital role to play in adopting environmentally responsible practices and incorporating ecological preservation into their strategies and operations. This requires a shift in the corporate mindset towards long-term sustainability rather than short-term profits.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Resistance to change can also hinder progress in ecological preservation. Some individuals, communities, and organizations may resist adopting sustainable practices due to concerns about costs, lack of awareness, or a resistance to change ingrained habits.
Addressing this challenge involves raising awareness about the importance of ecological preservation, providing education and training, and highlighting the benefits of sustainable practices. By demonstrating the economic, social, and environmental advantages of ecological preservation, it becomes easier to overcome resistance and foster a widespread commitment to sustainable development.
Education and Awareness for Ecological Preservation
Education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting ecological preservation and driving behavior change. By providing information, knowledge, and skills, individuals can make informed decisions and take actions that contribute to environmental sustainability.
Environmental Education in Schools
Environmental education in schools is essential for fostering a sense of environmental responsibility and sustainability among young generations. It involves integrating environmental topics into the curriculum, providing hands-on learning experiences, and promoting a deep understanding of ecological systems.
By incorporating environmental education into schools, students can develop critical thinking skills, become environmentally conscious individuals, and be equipped to address the challenges of ecological preservation in the future.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are an effective tool for mobilizing individuals and communities towards ecological preservation. These campaigns raise awareness about environmental issues, highlight the importance of sustainable practices, and encourage individuals to take action.
Public awareness campaigns can utilize various mediums, including traditional media, social media, and community events, to reach a wide audience. By disseminating information, inspiring behavioral change, and engaging individuals, these campaigns can contribute to the collective effort towards ecological preservation.
Role of Media and Technology
Media and technology play a vital role in spreading knowledge and promoting ecological preservation. Through documentaries, articles, and news coverage, media platforms can raise awareness about environmental issues and inspire action.
Furthermore, technology can facilitate data collection, analysis, and monitoring efforts, enhancing our understanding of ecological systems and aiding conservation efforts. Remote sensing, data modeling, and citizen science platforms are examples of technological advancements that have revolutionized ecological preservation.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations are essential for promoting ecological preservation. They provide a framework for sustainable practices, set standards, and incentivize environmentally friendly behaviors.
Environmental Laws and Regulations
Environmental laws and regulations establish the legal framework for ecological preservation. They address issues such as pollution control, waste management, the protection of biodiversity and natural resources, and the promotion of renewable energy.
By enacting and enforcing environmental laws and regulations, governments can ensure compliance with sustainable practices and provide a basis for holding individuals and organizations accountable for their environmental impact.
International Cooperation on Climate Change
International cooperation on climate change is critical for addressing the global challenges of ecological preservation. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to limit global warming and mitigate climate change through collective action and commitment.
Through these agreements, nations can agree on targets, share best practices, and collaborate on research and development efforts. By fostering international cooperation, governments can amplify their efforts towards ecological preservation and promote global environmental sustainability.
Incentives for Green Practices
Governments can also provide incentives for green practices to encourage individuals, businesses, and communities to adopt sustainable behaviors. These incentives can take the form of tax breaks, grants, subsidies, or preferential treatment for environmentally responsible practices.
By offering incentives, governments can stimulate investment in green technologies, energy-efficient practices, and sustainable resource management. These incentives help to offset the costs associated with transitioning to sustainable practices and promote the growth of environmentally friendly industries.
Monitoring and Evaluation in Ecological Preservation
Monitoring and evaluation play a crucial role in ecological preservation efforts. By assessing the effectiveness of conservation projects, monitoring changes in ecological health, and analyzing data, we can make informed decisions and implement evidence-based strategies.
Assessing Environmental Impact
Monitoring the environmental impact of human activities is essential for understanding and addressing their effects on ecosystems. Environmental impact assessments analyze the potential impacts of development projects, industry practices, or policy decisions on the environment.
By assessing environmental impact, we can identify potential risks, propose mitigation measures, and ensure that ecological preservation considerations are integrated into decision-making processes.
Indicators for Ecological Health
Indicators for ecological health provide a means to measure and assess the condition of ecosystems. These indicators can include measures of biodiversity, ecosystem services, habitat quality, water and air quality, and pollution levels.
By monitoring these indicators, we can track changes over time, identify areas of concern, and gauge the effectiveness of conservation strategies. These indicators also facilitate communication and understanding of ecological health among policymakers, scientists, and the general public.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection and analysis are fundamental for ecological preservation efforts. By collecting accurate and reliable data, we can gain insights into ecological processes, monitor biodiversity trends, and assess the effectiveness of conservation initiatives.
Advancements in technology, such as remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS), and citizen science platforms, have greatly facilitated data collection and analysis. These tools allow for the collection of large-scale spatial and temporal data, aiding in the identification of priority areas for conservation and helping to inform decision-making processes.
Conclusion
Ecological preservation, zero emissions, and biodiversity conservation are closely interconnected and fundamental for achieving a sustainable future. It requires the collaboration and commitment of governments, businesses, communities, and individuals to adopt sustainable practices, protect ecosystems, and preserve biodiversity.
By understanding the importance of ecological preservation, implementing zero emissions strategies, and prioritizing biodiversity conservation, we can ensure the long-term health and resilience of our planet. It is a collective responsibility to safeguard the environment for future generations and create a sustainable future where ecological preservation is prioritized alongside economic and social development. Let us embrace this responsibility and work together to achieve a harmonious balance between human activities and the natural world.