In this article, we will be discussing zero emission landscaping techniques that can contribute to clean air. You will learn about various strategies and practices that can be implemented to reduce emissions and improve air quality in your outdoor spaces. From choosing the right plants to utilizing alternative fuel equipment, these techniques will help you create a healthier and more sustainable environment. So, if you’re interested in making a positive impact and enjoying clean air in your surroundings, keep reading to discover how you can achieve it through zero emission landscaping techniques.

This image is property of www.bhg.com.
What is Zero Emission Landscaping?
Zero emission landscaping refers to the use of sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in landscaping to reduce or eliminate the emission of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. This approach focuses on minimizing the use of fossil fuels and adopting alternative methods that contribute to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
Defining Zero Emission Landscaping
Zero emission landscaping encompasses a variety of techniques that aim to minimize or eliminate the emission of pollutants from landscaping activities. By adopting these practices, you can significantly reduce the air pollution typically associated with traditional landscaping methods. These practices include the use of electric lawn equipment, battery-powered tools, manual tools, organic fertilizers, composting, natural pest control, xeriscaping, rainwater harvesting, and the incorporation of native plants.
Importance of Zero Emission Landscaping
Zero emission landscaping is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to combat air pollution, which is a major environmental and public health concern. By reducing emissions from landscaping activities, we can contribute to cleaner air and reduce the adverse effects of air pollution on human health. Secondly, zero emission landscaping promotes sustainability by minimizing the reliance on fossil fuels and non-renewable resources. Lastly, incorporating these practices into your landscaping routine can create a positive impact on the environment by conserving water, reducing waste, and preserving natural habitats.
Benefits of Zero Emission Landscaping
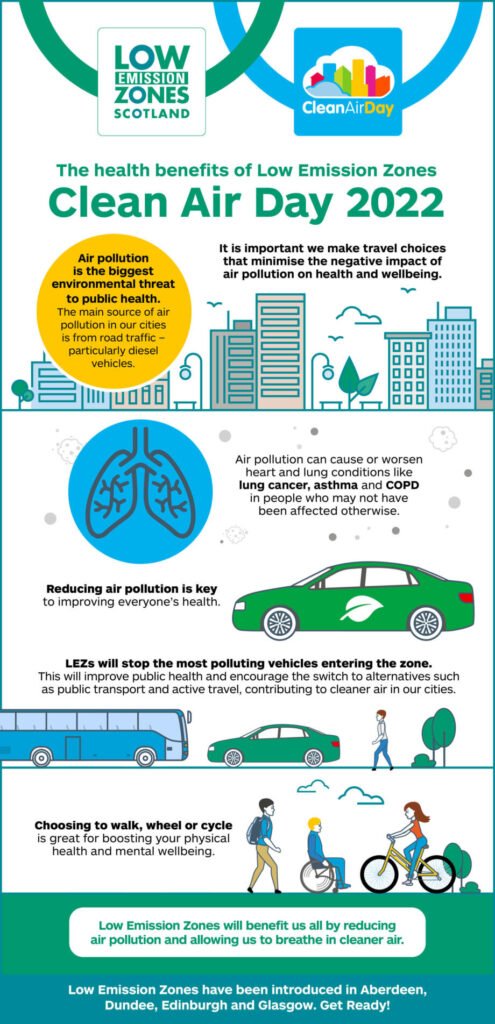
Reduced Air Pollution
One of the primary benefits of zero emission landscaping is the significant reduction in air pollution. Traditional landscaping practices that involve gasoline-powered machines, such as lawnmowers and leaf blowers, contribute to the emission of pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants not only harm the environment but also have detrimental effects on human health. By transitioning to zero emission landscaping techniques, you can help minimize these harmful emissions and contribute to cleaner air.
Improved Air Quality
Reducing air pollution through zero emission landscaping has a direct impact on air quality. By using electric lawn equipment, battery-powered tools, and manual tools, you can eliminate the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. Consequently, this helps improve the quality of the air that we breathe, leading to better respiratory health and reducing the risk of respiratory illnesses for both residents and wildlife in the area.
Health Benefits
Zero emission landscaping techniques also offer several health benefits. By reducing air pollution and improving air quality, we can improve respiratory health and minimize the risk of respiratory diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, and allergies. Additionally, limiting the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in favor of organic alternatives can reduce the exposure to harmful toxins, promoting a healthier environment for humans, pets, and beneficial insects.
Environmental Benefits
Zero emission landscaping practices have significant environmental benefits. By adopting these techniques, you contribute to the conservation of water resources through practices like xeriscaping and rainwater harvesting. Water-efficient landscaping techniques minimize water usage, reduce strain on water sources, and help combat drought conditions. Additionally, incorporating native plants in your landscaping helps preserve local biodiversity, provides habitats for wildlife, and supports the ecosystem.
Sustainability
Zero emission landscaping is an essential component of sustainable living. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels and adopting alternative methods, we can contribute to a more sustainable future. The use of electric lawn equipment, battery-powered tools, and manual tools significantly reduces our carbon footprint. Additionally, practices like composting and utilizing organic fertilizers promote the efficient use of resources, reduce waste, and create a closed loop system in landscaping, making it more sustainable in the long run.

This image is property of arborgold.com.
Techniques for Implementing Zero Emission Landscaping
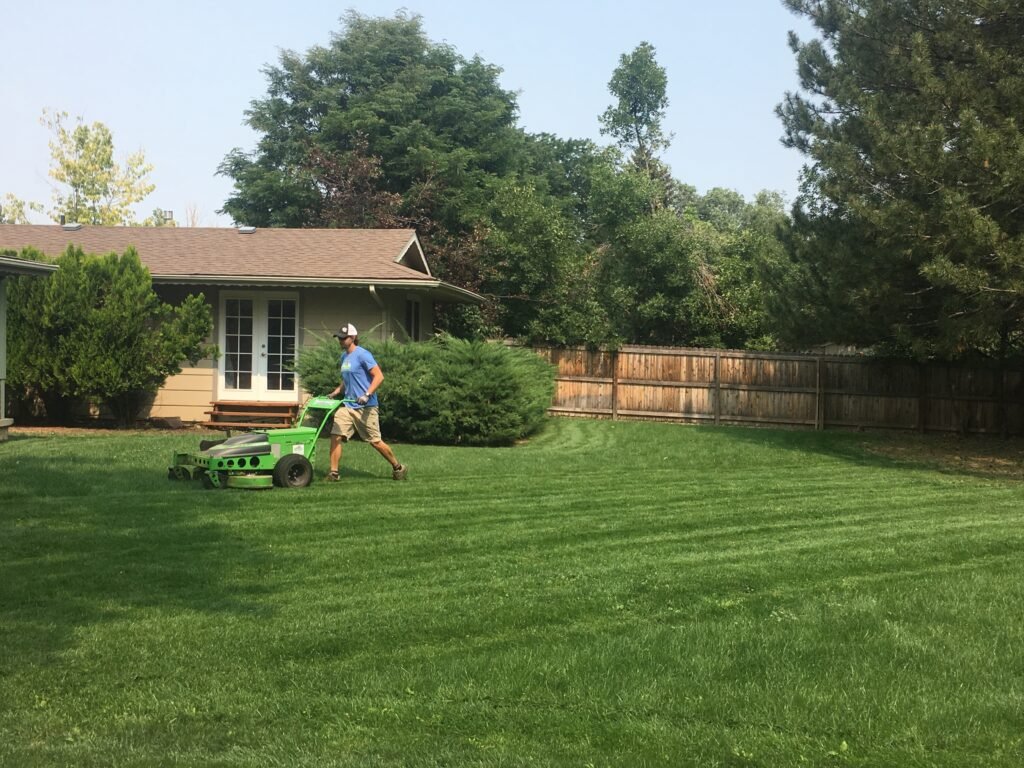
Electric Lawn Equipment
Electric lawn equipment, such as lawnmowers, trimmers, and leaf blowers, is an excellent alternative to their gasoline-powered counterparts. They operate on electricity, which significantly reduces emissions and air pollution. Electric lawn equipment is quieter, efficient, and easy to maintain. By investing in electric alternatives, you can make a substantial impact in reducing your carbon footprint and improving air quality.
Battery-Powered Tools
Battery-powered tools offer the convenience and mobility of gasoline-powered tools without the harmful emissions. These tools, such as hedge trimmers, chainsaws, and pruners, operate on rechargeable batteries, making them a reliable and eco-friendly option. By using battery-powered tools, you can reduce noise pollution, minimize air pollution, and enjoy the freedom of cordless operation.
Manual Tools
Manual tools are a great way to reduce emissions altogether. Tools like hand pruners, rakes, and shovels require physical effort but offer numerous benefits. They are silent, emit no pollution, and provide an opportunity for physical activity while maintaining your landscape. By incorporating manual tools into your landscaping routine, you can reduce your ecological footprint and stay active at the same time.
Organic Fertilizers
Using organic fertilizers instead of synthetic chemical fertilizers is an essential aspect of zero emission landscaping. Organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources, provide essential nutrients to plants without the harmful side effects associated with synthetic alternatives. Organic fertilizers improve soil health, promote microbial activity, and reduce the risk of leaching chemicals into groundwater, resulting in a healthier environment for plants, animals, and humans.
Composting
Composting is a natural recycling process that converts organic waste into nutrient-rich compost. By composting yard waste and kitchen scraps, you can create a valuable resource for your garden while reducing waste that would otherwise end up in landfills. Compost helps improve soil structure, increases water retention, and provides essential nutrients to plants. By utilizing compost in your landscaping, you can enrich the soil, support plant growth, and minimize the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Natural Pest Control
Natural pest control techniques are an important aspect of zero emission landscaping. Rather than relying on chemical pesticides, you can control pests by attracting beneficial insects and using plant-based pest repellents. Beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, prey on pests without harming plants or the environment. Planting pest-repellent herbs like basil and marigolds can help deter pests naturally, ensuring a healthy and balanced ecosystem in your garden.
Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping is an innovative landscaping technique that focuses on conserving water and utilizing drought-tolerant plants. By using native plants, mulch, and efficient irrigation systems, xeriscaping reduces water usage, minimizes maintenance needs, and eliminates the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Xeriscaping not only promotes water conservation but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of your landscape while supporting local biodiversity.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting involves capturing and storing rainwater for later use in landscaping. This technique helps conserve water and reduces reliance on municipal water supplies. Rainwater can be collected from rooftops and directed into storage tanks or underground reservoirs. It can then be used for irrigation, reducing the need for treated water. By implementing rainwater harvesting systems, you can reduce water consumption, decrease water bills, and ensure a sustainable water source for your landscaping needs.
Native Plants
Incorporating native plants into your landscaping is a crucial component of zero emission landscaping. Native plants are best suited to the local climate, require less water and maintenance, and provide a habitat for local wildlife. By selecting native plants, you promote biodiversity, contribute to wildlife conservation, and create a natural and sustainable landscape. Native plants also tend to be more resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Electric Lawn Equipment
Advantages of Electric Equipment
Electric lawn equipment offers several advantages compared to gasoline-powered alternatives. Firstly, they produce zero emissions during operation, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier environment. Electric equipment is also quieter, reducing noise pollution in residential areas. Additionally, electric tools are easier to start, require less maintenance, and are generally more cost-effective in the long run.
Types of Electric Lawn Equipment
Some common types of electric lawn equipment include electric lawnmowers, hedge trimmers, leaf blowers, and string trimmers. Electric lawnmowers come in both corded and cordless versions and provide efficient cutting power for small to medium-sized lawns. Hedge trimmers, leaf blowers, and string trimmers are available in corded and cordless options, offering versatility and convenience for various landscaping tasks.
Best Practices for Using Electric Equipment
To make the most of your electric lawn equipment, follow these best practices:
- Keep your equipment clean and free from debris to ensure optimal performance.
- Read the manufacturer’s instructions and follow the recommended maintenance schedule.
- Use appropriate extension cords for corded equipment and avoid overloading circuits.
- Charge battery-powered tools fully before use and store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Use the appropriate cutting height and technique for your lawn to promote healthy grass growth.
- Regularly inspect and sharpen cutting blades to maintain efficient cutting performance.

This image is property of www.bhg.com.
Battery-Powered Tools
Benefits of Battery-Powered Tools
Battery-powered tools offer several benefits compared to gasoline-powered options. Firstly, they produce zero emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier environment. They operate silently, reducing noise pollution and allowing for quieter landscaping activities. Battery-powered tools are also lightweight, portable, and easy to maneuver, providing users with greater flexibility and convenience.
Common Battery-Powered Tools
Common battery-powered tools include hedge trimmers, chainsaws, pole saws, leaf blowers, and string trimmers. Hedge trimmers provide precise trimming and shaping of hedges and shrubs, while chainsaws and pole saws offer efficient cutting power for tree branches and limbs. Leaf blowers assist in clearing leaves and debris from lawns and driveways, and string trimmers help maintain the edges of lawns. All these tools operate on rechargeable batteries, eliminating the need for gasoline and reducing emissions.
Proper Maintenance of Batteries
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of battery-powered tools, it’s essential to maintain the batteries properly. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place to prevent overheating and extend their lifespan.
- Charge batteries fully before use to maximize their runtime.
- Regularly inspect the battery for signs of damage or wear and replace if necessary.
- Clean battery terminals with a cloth or brush to remove dust and debris.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for battery maintenance and periodic replacement.
Manual Tools
Benefits of Using Manual Tools
Using manual tools for landscaping provides numerous benefits. Firstly, they produce zero emissions and operate silently, contributing to cleaner air and a quieter environment. Manual tools are also cost-effective, as they do not require fuel or electricity to operate. Additionally, using manual tools provides an opportunity for physical activity, helping you stay active while maintaining your landscape.
Common Manual Landscaping Tools
Some common manual tools used in landscaping include hand pruners, rakes, shovels, and hoes. Hand pruners are suitable for trimming small branches and stems, while rakes are effective for collecting leaves and debris. Shovels are versatile tools used for digging, planting, and moving soil. Hoes help control weeds and cultivate the soil. These manual tools offer excellent precision and control, allowing for efficient and eco-friendly landscaping.
Techniques for Efficient Manual Landscaping
To make the most of manual tools and ensure efficient landscaping, consider the following techniques:
- Use sharp and well-maintained tools to reduce effort and achieve clean cuts or digging.
- Choose ergonomic tools with comfortable handles and grips to minimize strain on your hands and back.
- Take breaks when needed and stay hydrated to prevent fatigue and ensure safety.
- Plan your landscaping tasks strategically to maximize energy and time efficiency.
- Utilize proper techniques, such as using your legs instead of your back when lifting heavy objects or applying consistent and even pressure when using hand tools.
- Monitor weather conditions and avoid working during extreme heat or inclement weather.

This image is property of www.bhg.com.
Organic Fertilizers
Importance of Organic Fertilizers
Using organic fertilizers in landscaping provides several benefits for both plants and the environment. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, such as plants, animals, and minerals, and are free from synthetic chemicals. They provide essential nutrients to plants while improving soil structure, promoting microbial activity, and enhancing water retention. Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, reducing the risk of nutrient leaching and groundwater contamination. Additionally, organic fertilizers help build a healthy and balanced ecosystem, supporting beneficial microorganisms and minimizing the negative impact on wildlife and water bodies.
Types of Organic Fertilizers
Several types of organic fertilizers are available for use in landscaping. Some examples include compost, manure, worm castings, bone meal, blood meal, and fish emulsion. Compost is a nutrient-rich soil amendment created through the decomposition of organic matter. Manure from herbivorous animals is an excellent source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Other organic fertilizers, such as bone meal and blood meal, provide essential micronutrients to plants. Fish emulsion is derived from fish waste and is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Application Best Practices
To ensure effective and efficient application of organic fertilizers, consider the following best practices:
- Test your soil to determine its nutrient levels and pH to make informed decisions about fertilizer type and application rate.
- Apply organic fertilizers during the appropriate time of year and incorporate them into the soil according to the product instructions.
- Avoid over-fertilization, as excessive nutrients can harm plants, cause nutrient runoff, and pollute water bodies.
- Follow the recommended application rates to achieve optimal results without risking damage to plants or the environment.
- Top-dress or side-dress organic fertilizers around the base of the plants, avoiding direct contact with leaves or stems.
- Water the area after fertilization to help distribute the nutrients and prevent the risk of fertilizer burn.
Composting
Benefits of Composting
Composting is a sustainable and environmentally friendly practice that offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it reduces waste by diverting organic materials from landfills. Composting also helps improve soil structure, water retention, and overall soil health. It enhances microbial activity and promotes the growth of beneficial organisms. Compost provides essential nutrients to plants, reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, and contributes to healthier and more productive gardens. Additionally, by composting, you create a closed-loop system that reduces the reliance on external resources and minimizes your ecological footprint.
Composting Methods
There are several composting methods to choose from, depending on your preferences and available space:
- Traditional composting: This method involves creating a compost pile or bin in your backyard. It requires mixing organic materials, such as yard waste and kitchen scraps, in specific ratios and allowing them to decompose over time. Regular turning or aerating of the pile promotes decomposition.
- Vermicomposting: Vermicomposting involves using worms, typically red wigglers, to decompose organic waste. Worms consume the organic matter, and their castings, known as vermicompost, provide a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
- Bokashi composting: Bokashi composting utilizes anaerobic fermentation to decompose organic waste. This method involves layering organic waste with a bokashi bran, which contains beneficial microbes that break down the waste. The fermented waste can then be buried in the soil or added to a traditional compost pile.
Utilizing Compost in Landscaping
Compost can be utilized in various ways to improve your landscape:
- Soil amendment: Mix compost into garden beds or apply it as a top dressing to enhance soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. Compost provides slow-release nutrients, improves drainage in heavy soils, and increases water-holding capacity in sandy soils.
- Mulch: Use compost as a natural mulch around plants to help suppress weeds, conserve soil moisture, and regulate soil temperature. Compost mulch gradually breaks down, enriching the soil and providing a continuous supply of nutrients to the plants.
- Potting mix: Mix compost with other organic materials, such as perlite or coconut coir, to create a nutrient-rich potting mix. This mix provides plants with essential nutrients and promotes healthy root development in container gardening.
- Compost tea: Brewing compost tea by steeping compost in water helps extract beneficial microbes and nutrients. The resulting liquid can be used as a liquid fertilizer or foliar spray to promote plant health and improve nutrient uptake.

This image is property of cleanairlawncare.com.
Natural Pest Control
Role of Natural Pest Control
Natural pest control focuses on managing pests using environmentally friendly and non-toxic methods. It aims to minimize the use of chemical pesticides, which can harm beneficial insects, animals, and the environment. By implementing natural pest control techniques, you can maintain a balanced ecosystem, control pest populations, and protect your plants without harming beneficial organisms.
Beneficial Insects
Beneficial insects play a crucial role in natural pest control. They prey on pests, consume their eggs or larvae, and help regulate pest populations. Some common beneficial insects include ladybugs, lacewings, praying mantises, and hoverflies. Attracting these insects to your garden can be achieved by providing suitable habitats with a variety of flowers, native plants, and shelter. Avoid using chemical pesticides that can harm beneficial insects and disrupt the ecological balance.
Plant-Based Pest Repellents
Many plants have natural properties that repel pests. By incorporating these plants into your landscaping, you can help deter pests naturally. Some example plants with pest repellent properties include basil, rosemary, marigolds, catnip, and garlic. Planting these pest-repellent herbs and flowers around your garden or in close proximity to susceptible plants can discourage pests from infesting and damaging your landscape. Additionally, essential oils derived from these plants can be used as natural insect repellents or for making DIY pest control sprays.
Xeriscaping
Exploring Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping is a landscaping technique that focuses on creating water-efficient and sustainable gardens. It is particularly beneficial in arid and drought-prone regions. Xeriscaping aims to reduce water usage, conserve resources, and promote the use of native and drought-tolerant plants. By implementing xeriscaping techniques, you can create a visually appealing landscape while minimizing water requirements and maintenance needs.
Water-Efficient Landscaping Techniques
Some water-efficient techniques commonly used in xeriscaping include:
- Selecting drought-tolerant plants: Choose plants that are adapted to the local climate and require minimal watering once established. Native plants are often excellent options, as they are adapted to the local environment and resistant to pests and diseases.
- Grouping plants with similar water needs: Place plants with similar water requirements together to ensure efficient water usage. This prevents overwatering or underwatering plants and helps create a more effective irrigation system.
- Using mulch: Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or bark, around plants and in garden beds. Mulch helps retain moisture in the soil, reduces weed growth, and regulates soil temperature.
- Efficient irrigation: Implement water-efficient irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation or soaker hoses, to deliver water directly to the root zone of plants. Avoid using sprinklers that can result in wasteful evaporation and inefficient water distribution.
- Soil improvement: Amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost, to improve water retention and ensure proper drainage. Well-amended soil retains water longer, reducing the need for frequent watering.
Designing a Xeriscape Garden
When designing a xeriscape garden, consider the following elements:
- Grouping plants according to their watering needs and sun exposure requirements.
- Creating efficient irrigation zones based on plant water requirements.
- Incorporating landscape features like rocks, gravel, and ornamental grasses to reduce water usage and add visual interest.
- Designing pathways and hardscapes with materials that allow water penetration and minimize runoff.
- Considering the use of rainwater harvesting systems to collect and store water for irrigation use.
- Maintaining a balance between hardscape and softscape elements to create an aesthetically pleasing and water-efficient landscape.
Rainwater Harvesting
Utilizing Rainwater in Landscaping
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater for future use, primarily in landscaping. It is an effective method to conserve water, reduce reliance on municipal sources, and ensure a sustainable water supply. By implementing rainwater harvesting systems, you can utilize nature’s gift to water your plants and reduce water bills.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
There are several types of rainwater harvesting systems to choose from, depending on your needs and available space:
- Rain barrels: Rain barrels are an excellent option for small-scale rainwater harvesting. They typically capture rainwater from downspouts and store it in a barrel or container. The water can then be used for various purposes, including watering plants, filling birdbaths, or washing outdoor equipment.
- Cisterns: Cisterns are larger storage tanks that collect and store rainwater from rooftops or other collection surfaces. They provide a more substantial water storage capacity and can be used for irrigation purposes throughout the year. Cisterns can be above ground or underground, depending on space availability and aesthetic preferences.
- Rain gardens: Rain gardens are specially designed landscaping features that capture and filter rainwater runoff. They are typically planted with native, water-loving plants and utilize a mixture of soil and mulch to absorb and filter rainwater before it enters the ground.
Maintenance of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
To ensure the effectiveness and longevity of your rainwater harvesting system, regular maintenance is essential:
- Clean gutters and downspouts regularly to prevent debris from clogging the system.
- Inspect and clean rain barrels or cisterns periodically to remove any sediment or organic matter that may accumulate.
- Use mesh screens or filters to prevent mosquito breeding and keep the water clean.
- Ensure proper drainage from rain gardens to prevent standing water and potential mosquito breeding grounds.
- Regularly check for leaks or damage in the system and promptly repair any issues.
- Consider additional filtration or treatment methods, such as using charcoal filters or UV sterilizers, if the water will be used for potable purposes.
Native Plants
Benefits of Native Plants
Incorporating native plants into your landscaping offers numerous benefits:
- Adapted to the local climate: Native plants are naturally adapted to the local climate, including temperature, rainfall patterns, and soil conditions. They are more likely to survive and thrive in their native environment, requiring less water, fertilizer, and maintenance.
- Biodiversity preservation: Native plants support local ecosystems and provide habitat for native wildlife, including birds, butterflies, and bees. By including native plants in your landscape, you contribute to biodiversity conservation and help restore natural habitats.
- Pest and disease resistance: Native plants have evolved to withstand local pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions. They are often more resistant to pests and diseases compared to non-native species, resulting in less reliance on synthetic pesticides.
- Water conservation: Native plants are typically drought-tolerant and adapted to local rainfall patterns. Their deep root systems help improve soil structure and water infiltration, reducing water runoff and increasing water retention.
- Low maintenance: Once established, native plants generally require less maintenance compared to non-native species. They are well-adapted to the local environment and often have lower water, fertilizer, and trimming needs.
Choosing Native Plants
When selecting native plants for your landscape, consider the following factors:
- Local climate and growing conditions: Choose plants that are adapted to the specific climate, soil type, and sunlight conditions in your region. Native plant nurseries and local gardening resources can provide guidance on the best native species for your area.
- Plant diversity: Incorporate a variety of native plants to support a diverse range of beneficial insects, attract pollinators, and create an aesthetically pleasing landscape.
- Wildlife habitat: Select plants that provide food, shelter, and nesting sites for local wildlife. Consider the needs of birds, butterflies, bees, and other beneficial insects when choosing native plants.
- Seasonal interest: Choose native plants that offer visual interest throughout the year, with blooming periods, fall foliage, or interesting seed heads.
Creating Habitat for Native Wildlife
To create a welcoming habitat for native wildlife, follow these tips:
- Plant a diverse range of native plants that provide food sources (flowers, fruits, seeds), shelter (dense foliage, birdhouses), and nesting sites (brush piles, nesting boxes).
- Provide a water source, such as a birdbath or small pond, to attract birds, butterflies, and other wildlife.
- Avoid the use of chemical pesticides and herbicides, which can harm beneficial insects and wildlife.
- Leave dead wood or fallen leaves as natural habitats for beneficial insects and provide nesting materials for birds.
- Install bat boxes or bee hotels to encourage the presence of these pollinators.
Conclusion
Implementing zero emission landscaping techniques is an effective way to make a positive impact on air quality, promote sustainability, and encourage eco-friendly practices. By incorporating electric lawn equipment, battery-powered tools, manual tools, organic fertilizers, composting, natural pest control, xeriscaping, rainwater harvesting, and native plants into your landscaping routine, you can reduce air pollution, improve air quality, enhance environmental health, and contribute to a more sustainable future. By embracing these techniques, you not only improve the aesthetics of your outdoor space but also create a healthier, cleaner, and more sustainable environment for yourself, your community, and future generations.