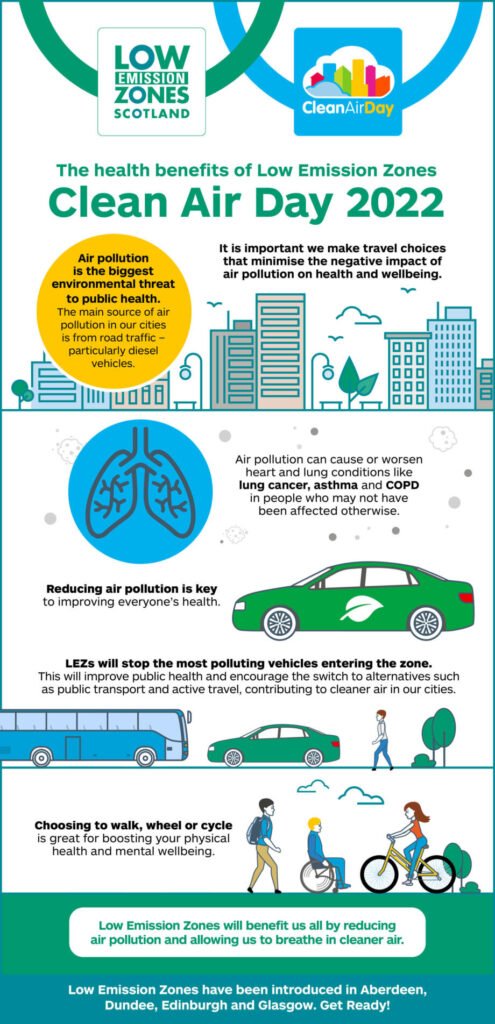
If you’ve ever wondered how to tackle the issue of flooding in your area, look no further than rain gardens. These innovative gardens are not only aesthetically pleasing but also serve a crucial role in preventing flooding. By harnessing the power of rainwater, these gardens act as natural reservoirs, allowing water to be absorbed and filtered before being released into the surrounding environment. In this article, we will explore the key principles of creating effective rain gardens for flooding prevention, providing you with the knowledge and inspiration to make a positive impact in your community.
Choosing the Right Site for a Rain Garden
Assessing the Existing Drainage
When choosing a site for your rain garden, it is crucial to assess the existing drainage conditions. Look for areas in your yard where water tends to collect or where there are signs of poor drainage, such as persistent puddles or saturated soil. These areas are ideal for installing a rain garden as they can effectively capture and manage excess water.
Identifying the Source of Water
To effectively design your rain garden, it’s important to identify the source of water that will be directed towards it. This can include roof runoff, downspouts, or areas of your yard where water tends to flow during heavy rains. Understanding the source of water will help you determine the size and shape of your rain garden to ensure it can accommodate the expected volume of water.
Considering the Surrounding Landscape
Take into consideration the surrounding landscape when choosing a site for your rain garden. Look for areas that are not near large trees or structures that may cause obstructions or interfere with the growth of the plants in your rain garden. Additionally, consider the proximity to your house and any nearby utility lines to ensure that digging and construction will not cause any issues.
Designing the Rain Garden
Determining the Size and Shape
The size and shape of your rain garden will depend on the amount of water you expect it to handle and the available space in your yard. A general rule of thumb is to aim for a rain garden depth of about 6 inches. The shape can be determined based on the space available and any existing landscaping features that you want to incorporate. Consider using gentle, curved edges to create an aesthetically pleasing design.
Calculating the Capture Area
To determine the size of your rain garden, you need to calculate the capture area. This is the area that will contribute water to your rain garden. Measure the square footage of your roof, driveway, or any other surfaces that will direct water towards the rain garden. Use this measurement to determine the appropriate size of your rain garden, keeping in mind that it should generally be about 20% of the capture area.
Creating the Infiltration Basin
The infiltration basin is an essential component of a rain garden. It is a depression in the ground that allows water to slowly percolate into the soil. Once you have determined the size and shape of your rain garden, you will need to excavate the soil to create the infiltration basin. This basin should be designed to hold the expected volume of water without overflowing, allowing it to gradually infiltrate the ground.
Selecting Suitable Plants
Native vs. Non-native Plants
When selecting plants for your rain garden, it is generally recommended to choose native species. Native plants are well adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, making them more likely to thrive in your rain garden. They also provide important habitat and food sources for local wildlife. Non-native plants may not have the same resilience and can sometimes become invasive, competing with native species.
Types of Plants for Rain Gardens
Rain gardens typically incorporate a mix of plants that can withstand periods of both drought and excessive moisture. Look for plants that have deep root systems, as they can help with water infiltration and erosion control. Grasses, sedges, and ferns are popular choices for rain gardens, as they have fibrous root systems that can efficiently absorb and filter water.
Considerations for Planting Depth
When planting in a rain garden, it’s important to consider the depth at which each plant should be placed. Some plants can tolerate wetter conditions and can be planted closer to the basin’s center, while others prefer drier conditions and should be placed towards the outer edges. By considering the unique needs of each plant, you can create a diverse and thriving rain garden ecosystem.
Preparing the Rain Garden Site
Clearing the Area
Before starting the construction of your rain garden, clear the area of any existing vegetation, debris, or weeds. This will allow you to have a clean and level surface to work with. Remove any grass or plants from the area and consider using this material for composting or mulching in other parts of your garden.
Excavating the Soil
After clearing the area, you will need to excavate the soil to create the necessary depth for your rain garden. Remove the top layer of soil and set it aside, as this can be used later to amend the soil. Dig the basin according to the size and shape determined during the design phase, making sure to create a gentle slope towards the center.
Amending the Soil
Once the rain garden has been excavated, it is important to amend the soil to improve drainage and provide nutrients for the plants. Mix the removed topsoil with compost or organic matter to improve its structure and fertility. This will help the plants establish and thrive in the rain garden environment.
Installing Drainage System
Types of Drainage Systems
Installing a drainage system can help manage excess water and prevent overflow in your rain garden. There are various types of drainage systems to choose from, including French drains, perforated drain pipes, or gravel-filled trenches. The specific system you choose will depend on factors such as soil type, water volume, and available space.
Proper Placement of Drain Pipes
When installing drain pipes in your rain garden, proper placement is crucial for effective water management. Position the drain pipes along the sides of the rain garden, slightly above the base of the basin. This will allow water to flow into the pipes and be directed away from the garden. Ensure that the pipes have a slight downward slope to facilitate water flow.
Ensuring Proper Slope and Gradient
To ensure proper water flow and prevent standing water in your rain garden, it is important to design and construct it with the proper slope and gradient. The slope should direct water towards the center of the garden where the infiltration basin is located, allowing it to slowly infiltrate the soil. Avoid steep slopes, as they can cause erosion and lead to soil displacement.
Creating Overflow and Outlet Structures
Determining the Location of Overflow
During heavy rainfall, it is essential to have an overflow structure in place to prevent excessive water accumulation in your rain garden. Determine the location for the overflow structure based on the surrounding landscape and the natural flow of water. This structure should be positioned to direct the overflow away from your house and any other sensitive areas.
Constructing the Overflow Structure
Constructing the overflow structure can be done using various materials such as concrete blocks or gravel-filled channels. The structure should be designed to allow water to flow over it when the rain garden reaches its maximum capacity. Consider adding vegetation or rocks around the overflow structure to enhance its visual appeal and blend it harmoniously with the rain garden’s design.
Installing the Outlet Pipe
In addition to the overflow structure, it is important to have an outlet pipe installed in your rain garden. This pipe will carry excess water away from the garden and prevent it from pooling or causing damage. Choose a location for the outlet pipe that will efficiently drain the water and ensure that it is securely connected to the drain pipes in the garden.
Mulching and Edging
Applying Mulch to the Rain Garden
Mulching your rain garden is an important step to help conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and improve the overall aesthetics of the garden. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or shredded bark, to the surface of the rain garden. Avoid applying mulch too close to the base of plants to prevent rotting or diseases.
Selecting Suitable Edging Materials
Edging your rain garden provides a neat and defined border, preventing erosion and maintaining the garden’s shape. Choose edging materials that are durable and can withstand moisture, such as stone, bricks, or plastic edging. Consider using materials that complement the overall design of your rain garden and create a visually pleasing transition between the garden and surrounding landscape.
Proper Edging Techniques
When edging your rain garden, ensure that the edging is installed securely and sunk into the ground to prevent runoff or displacement. Use a level to ensure that the edging is horizontal and create a smooth transition between the garden and the surrounding soil or lawn. Proper edging techniques will help maintain the integrity and aesthetics of your rain garden.
Establishing and Maintaining the Rain Garden
Planting the Rain Garden
Once the rain garden construction is complete, it’s time to plant the selected native plants. Dig individual planting holes based on the planting depth requirements of each plant and gently place them in the holes. Firmly pack the soil around the roots and water the plants thoroughly. Mulch around the plants to help retain moisture and prevent weed growth.
Watering and Fertilizing
In the initial stages of establishing your rain garden, regular watering is essential to help the plants establish their root systems. Water the garden deeply and infrequently to encourage deep root growth. Avoid excessive fertilization, as native plants in a rain garden typically do not require heavy feeding. Instead, focus on maintaining optimal soil moisture and organic matter content.
Regular Maintenance Practices
To ensure the long-term health and functionality of your rain garden, regular maintenance is necessary. This includes removing weeds, pruning dead or damaged plant material, and monitoring water levels during heavy rainfall events. Keep an eye out for any signs of erosion or soil settling, and address these issues promptly. By regularly maintaining your rain garden, you can maximize its effectiveness in preventing flooding and promoting healthy ecosystems.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Monitoring Water Levels
Regularly monitor the water levels in your rain garden, especially during heavy rainfall events. Observe how quickly the water infiltrates the soil and whether any standing water persists for longer than expected. If water levels are consistently high or drainage seems inadequate, it may be necessary to reassess the design and make adjustments such as adding an additional drainage system.
Identifying and Addressing Issues
Identifying and addressing issues in your rain garden promptly is crucial for its long-term success. Keep an eye out for signs of poor plant growth, pest infestations, or unusual water flow patterns. If you notice any issues, consult gardening resources or seek advice from local experts to determine the cause of the problem and implement appropriate solutions.
Seeking Professional Assistance
If you encounter complex issues or are unsure about certain aspects of your rain garden’s design or maintenance, do not hesitate to seek professional assistance. Local landscaping or gardening professionals can provide expert advice tailored to your specific situation. Their expertise and guidance can help ensure that your rain garden is effective in preventing flooding and thriving as a sustainable landscape feature.
Educating the Community
Outreach and Awareness Programs
To promote the benefits of rain gardens for flooding prevention, consider organizing outreach and awareness programs in your community. This can include hosting workshops, seminars, or webinars that educate residents about the importance of rain gardens and how to design and maintain them effectively. Engaging the community in these programs can foster a greater understanding and appreciation for sustainable stormwater management practices.
Demonstration Rain Gardens
Setting up demonstration rain gardens in public spaces can be a powerful way to showcase the benefits and functionality of these landscape features. Work with local organizations, schools, or municipalities to identify suitable locations and gain support for establishing demonstration rain gardens. These gardens can serve as educational tools, inspiring others in the community to adopt similar practices.
Providing Maintenance Workshops
Offering maintenance workshops specifically focused on rain gardens can help homeowners and gardeners enhance their knowledge and skills in managing these unique gardens. These workshops can cover topics such as seasonal maintenance, weed control, and plant selection. By empowering individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to maintain their rain gardens, you can contribute to the long-term success and effectiveness of these sustainable stormwater management solutions.
Creating effective rain gardens for flooding prevention requires careful planning, consideration of site conditions, and appropriate plant selection. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can design and maintain a rain garden that not only helps mitigate flooding but also creates a beautiful and ecologically beneficial landscape feature. Start by assessing your existing drainage, identifying water sources, and considering the surrounding landscape. Then, proceed to design and prepare the rain garden, selecting suitable plants and installing the necessary drainage systems. Taking the time to properly establish and maintain your rain garden will provide lasting benefits for both your property and the environment. Remember to monitor and troubleshoot any issues that may arise, and don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance or educate your community about rain gardens. With proper planning and ongoing care, your rain garden will become a valuable asset in preventing flooding and promoting a healthier ecosystem.