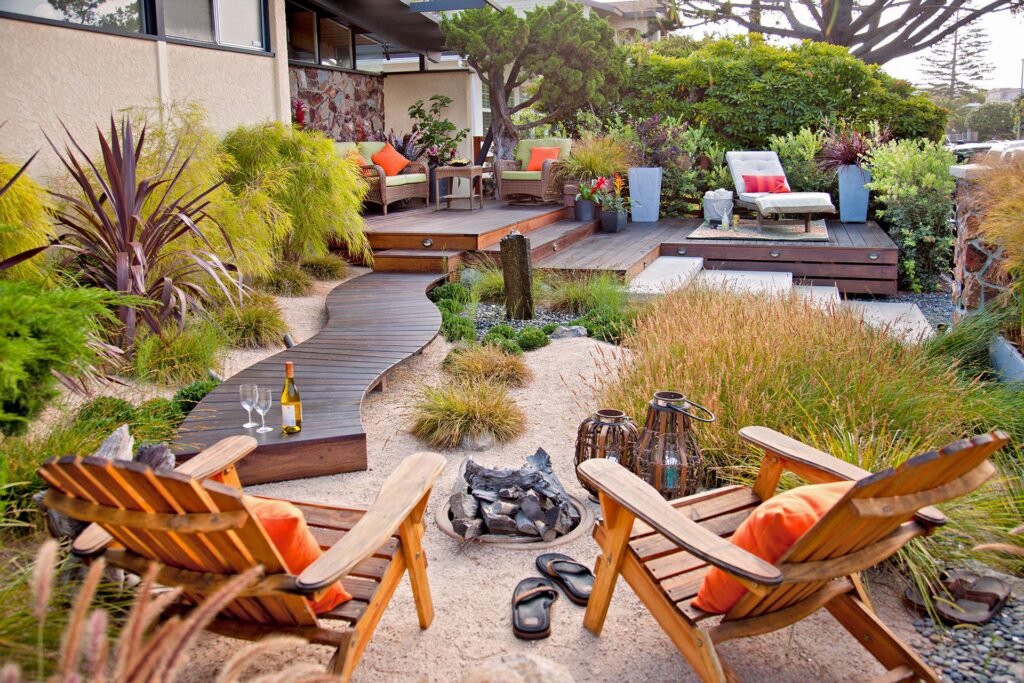
Are you looking to transform your small outdoor space into a sustainable and beautiful oasis? Look no further! This article will guide you on how to create sustainable landscapes in small spaces, offering practical tips and innovative ideas to make the most out of limited areas. From choosing the right plants and incorporating eco-friendly materials to maximizing space and creating a harmonious environment, you’ll discover how to design a small sustainable landscape that is both aesthetically appealing and environmentally conscious. Get ready to unleash your creativity and turn your compact yard into a thriving green haven!
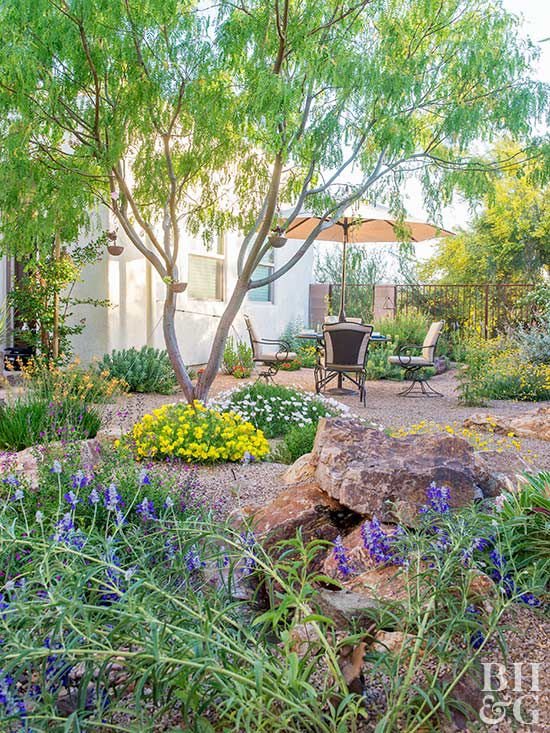

This image is property of www.bhg.com.
Designing a Sustainable Landscape
Designing a sustainable landscape for your outdoor space involves careful consideration and planning. By analyzing the space available and understanding your needs, you can create an environment that not only enhances the beauty of your home but also promotes sustainability. One of the first steps in this process is analyzing the space and identifying its unique characteristics and limitations.
Analyzing the space
When analyzing your outdoor space, take note of the size, shape, and topography of the area. Consider elements such as the amount of sunlight the area receives, the direction of prevailing winds, and any existing features like trees or structures. Understanding these factors will help you determine how to make the most of your space while efficiently utilizing resources.
Understanding the needs
Before embarking on any landscaping project, it is essential to identify your specific needs and desires for the outdoor space. Are you looking to create a peaceful retreat, a space for entertaining guests, or a functional area for gardening? By clearly defining your goals, you can design a landscape that meets your needs while incorporating sustainable practices.
Choosing native plants
Choosing native plants is a crucial aspect of sustainable landscaping. Native plants are adapted to the local climate and require less water, fertilizer, and pesticides than non-native species. They also provide habitat and food for local wildlife and can enhance biodiversity in your area. By incorporating native plants into your landscape, you not only support the local ecosystem but also reduce the need for excessive maintenance and resources.
Creating a focal point
Creating a focal point in your sustainable landscape can add visual interest and draw attention to specific areas. This can be achieved through the use of an eye-catching feature such as a water feature, sculpture, or striking plant arrangement. By carefully selecting and positioning a focal point, you can create a sense of harmony and balance in your outdoor space.
Maximizing the Use of Space
When working with small spaces, it’s important to maximize the use of every available inch. This can be achieved through various techniques such as vertical gardening, utilizing containers, and integrating functional elements.
Vertical gardening
Vertical gardening is an excellent solution for small spaces as it allows you to grow plants upwards, utilizing vertical surfaces such as walls or trellises. This technique not only saves space but also creates a visually appealing and vibrant display. You can grow various types of plants, including flowers, herbs, and even vegetables, using vertical gardening techniques.
Utilizing containers
Using containers is another effective way to maximize space in a small landscape. Containers can be placed on patios, balconies, or even hung from railings, allowing you to grow plants in areas where traditional gardening might not be possible. Choose containers that are proportionate to the size of your space and opt for lightweight ones that are easy to move around. This way, you can create a flexible and versatile landscape that suits your needs.
Integrating functional elements
Integrating functional elements, such as seating areas, pathways, or even built-in storage, can add both practicality and aesthetics to your small landscape. By carefully planning the placement of these elements, you can optimize the use of space while maintaining a cohesive and inviting atmosphere. Functional elements can serve multiple purposes, such as providing seating while also acting as planters or incorporating storage compartments for gardening tools.
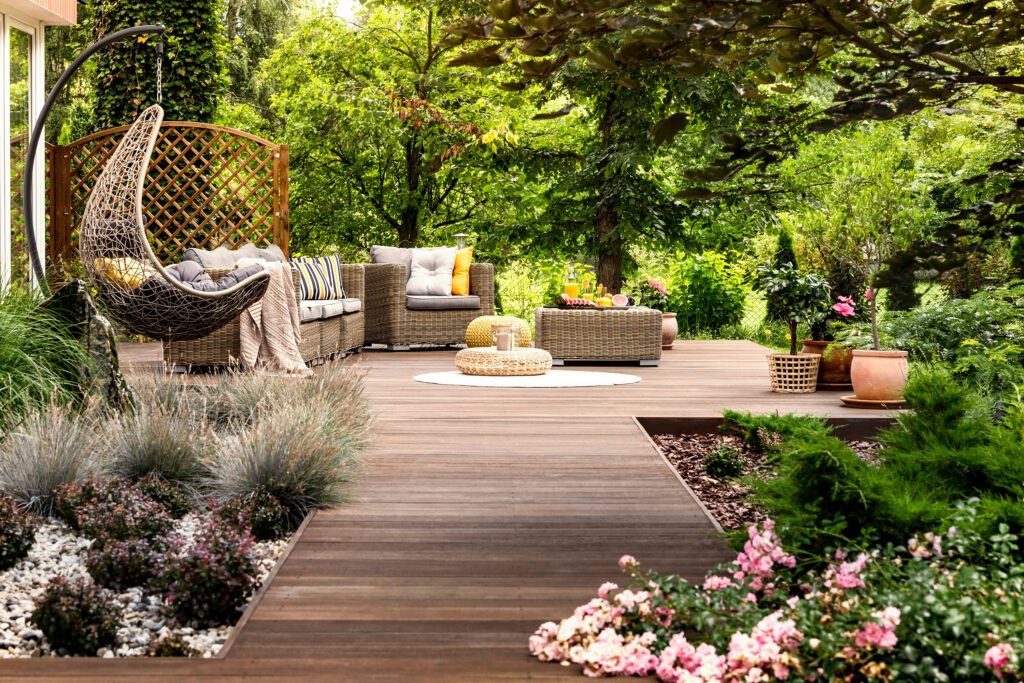

This image is property of cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net.
Conserving Water
Conserving water is a vital aspect of sustainable landscaping, especially in regions prone to drought or water scarcity. By implementing water-saving strategies, you can minimize water waste and contribute to the preservation of this precious resource.
Installing a drip irrigation system
Installing a drip irrigation system is an efficient and targeted way to deliver water to your plants. Unlike traditional watering methods, such as sprinklers, drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the root zones of plants, reducing evaporation and runoff. This method not only conserves water but also promotes healthier plant growth by preventing over or under-watering.
Using water-efficient plants
Choosing and planting water-efficient plants can significantly reduce water consumption in your landscape. Native plants are often naturally adapted to the local climate and require less water than non-native species. Additionally, drought-tolerant plants, succulents, and ornamental grasses are excellent choices for water conservation. Be sure to group plants with similar water requirements together, as this will allow for efficient watering.
Collecting and reusing rainwater
Collecting and reusing rainwater is another effective way to conserve water in your landscape. Install a rain barrel or cistern to capture rainwater from downspouts, and use this water for irrigation purposes. Not only does this practice reduce water consumption, but it also helps to prevent stormwater runoff, which can carry pollutants into nearby water bodies.
Promoting Biodiversity
Promoting biodiversity in your landscape creates a vibrant and thriving ecosystem. By attracting pollinators, providing habitat for wildlife, and creating a diverse plant community, you can support and strengthen the local environment.
Attracting pollinators
Pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds play a vital role in plant reproduction and overall ecosystem health. To attract these pollinators to your sustainable landscape, incorporate a variety of nectar-rich plants, vibrant flowers, and plants that provide food and shelter throughout the year. Providing a water source, such as a shallow birdbath with stones for perching, can also help attract pollinators.
Providing habitat for wildlife
Creating habitats for wildlife in your landscape is essential for promoting biodiversity. Incorporate features such as birdhouses, bat boxes, or butterfly feeders to provide shelter and food sources for various species. Consider leaving a portion of your landscape in a natural, untouched state to provide wildlife with adequate cover and nesting sites.
Creating a diverse plant community
A diverse plant community consisting of different species and plant types helps create a balanced and resilient ecosystem. Avoid planting a monoculture and instead incorporate a variety of plants with different heights, textures, and bloom times. This diversity attracts a broader range of wildlife, promotes natural pest control, and ensures that your landscape remains healthy and dynamic.
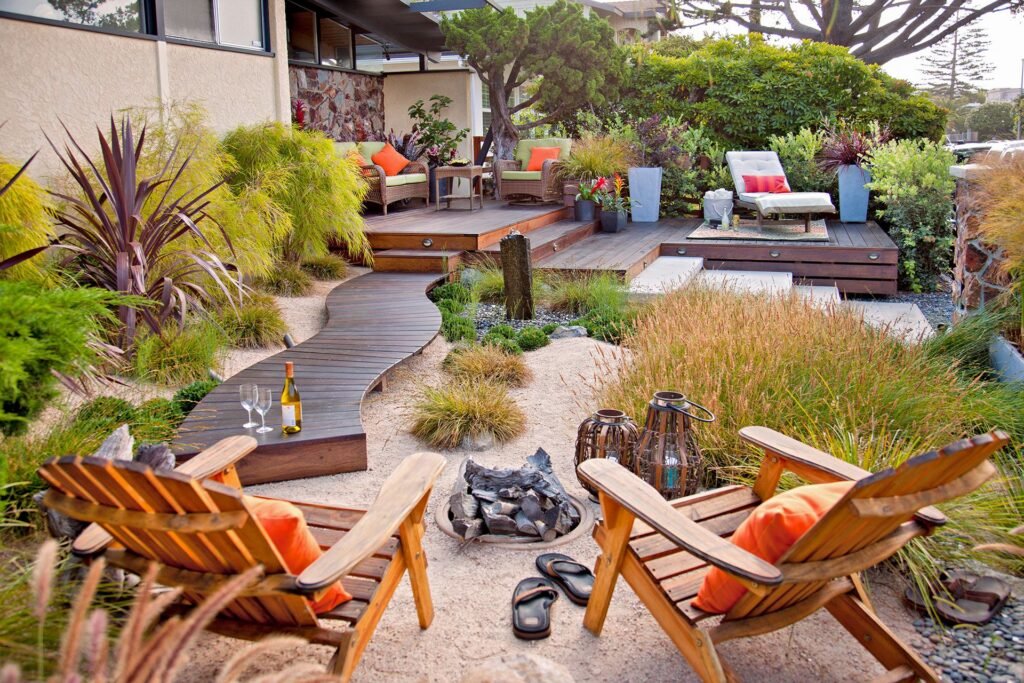

This image is property of www.bhg.com.
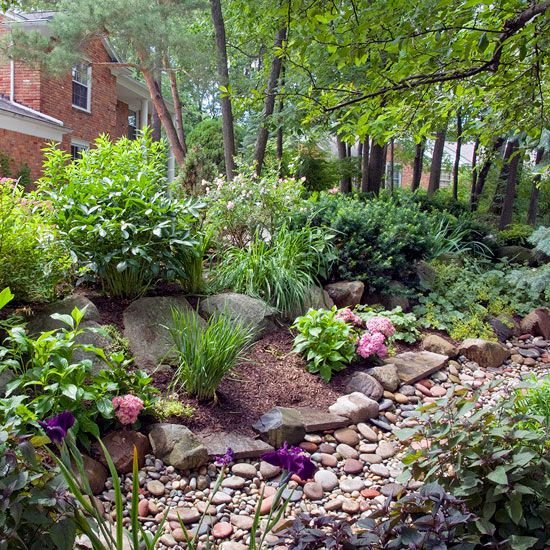
Managing Soil Health
Maintaining healthy soil is the foundation of a sustainable landscape. By amending the soil, practicing mulching, and preventing erosion, you can create an environment that supports plant growth and minimizes the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Amending the soil
Amending the soil with organic matter, such as compost, improves its structure and fertility. Organic matter enhances soil water retention, promotes aeration, and encourages beneficial microbial activity. Before planting, incorporate compost or well-rotted manure into the soil to provide essential nutrients and improve overall soil health.
Practicing mulching
Mulching provides numerous benefits for your landscape, including conserving soil moisture, suppressing weed growth, and regulating soil temperature. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around plants to retain moisture and prevent weed competition. As the mulch breaks down, it also adds organic matter to the soil, further enriching its fertility.
Preventing erosion
Erosion can lead to the loss of soil, nutrients, and organic matter from your landscape. To prevent erosion, use erosion control measures such as retaining walls, terraces, or swales. Planting groundcover plants with spreading root systems, like creeping thyme or ajuga, can also help stabilize soil and prevent erosion on slopes.
Reducing Maintenance Needs
Creating a low-maintenance landscape not only saves time and effort but also reduces the use of chemicals and resources. By choosing low-maintenance plants, implementing smart design strategies, and applying organic weed control methods, you can minimize the need for intensive maintenance.
Choosing low-maintenance plants
Selecting low-maintenance plants that are well-adapted to your local climate and soil conditions is key to reducing maintenance needs. Native plants and drought-tolerant species often require less watering and are more resistant to pests and diseases. Additionally, choose plants with a slow growth rate to minimize pruning requirements and opt for self-seeding or perennial plants that require less replanting.
Implementing smart design
Smart design strategies, such as grouping plants with similar water and sunlight requirements together, can reduce maintenance needs. This allows for efficient watering and reduces the risk of over or under-watering. Creating defined planting beds and incorporating mulch or landscape fabric around plants can also help suppress weed growth and reduce the need for frequent weeding.
Applying organic weed control
Using organic weed control methods is an effective way to minimize the need for synthetic herbicides. Hand-pulling weeds, using a hoe or cultivator, or applying organic mulch can help suppress weed growth and keep your landscape looking tidy. Regularly inspect and remove weeds before they have a chance to establish and spread.
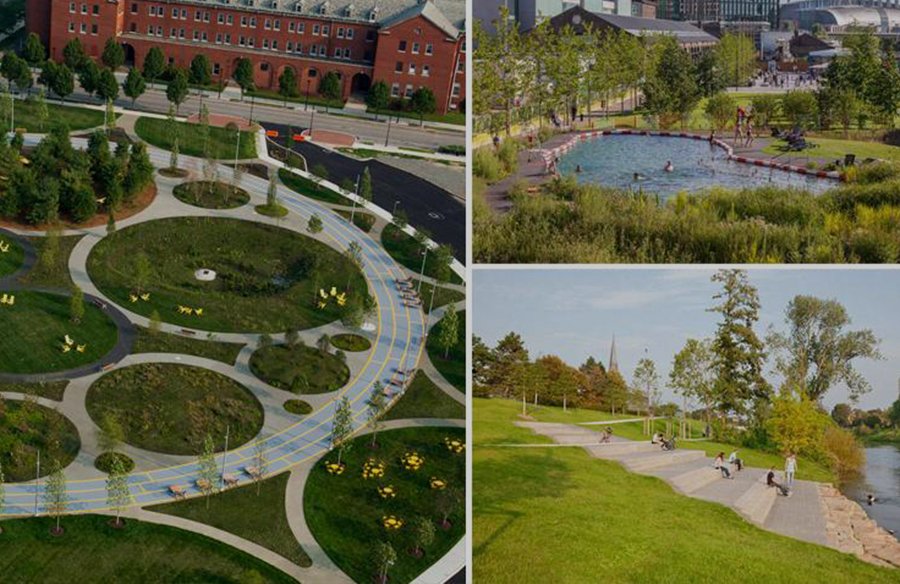

This image is property of www.re-thinkingthefuture.com.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Designing an energy-efficient landscape can help reduce energy consumption and contribute to a sustainable lifestyle. By using shade trees strategically, designing for passive cooling, and incorporating solar-powered features, you can enhance energy efficiency in your outdoor space.
Using shade trees strategically
Strategically planting shade trees can significantly reduce the cooling load on your home during hot summer months. Plant trees on the south and west sides of your house to provide shade and block direct sunlight from entering windows. Deciduous trees are an excellent choice as they provide shade in the summer while allowing sunlight to warm your home during the winter months.
Designing for passive cooling
Passive cooling techniques can help reduce reliance on air conditioning and lower energy consumption. Create natural ventilation by strategically placing windows or installing outdoor ceiling fans to facilitate air movement. Incorporate features such as pergolas or trellises covered in shade-loving vines to provide additional cooling and create comfortable outdoor spaces.
Incorporating solar-powered features
Incorporating solar-powered features in your landscape can further enhance energy efficiency. Install solar-powered outdoor lighting to illuminate pathways or seating areas. Consider incorporating a solar-powered water fountain or solar panels to generate electricity for outdoor appliances or devices. By harnessing the power of the sun, you can save energy and reduce your environmental footprint.
Minimizing Chemical Inputs
Minimizing the use of chemicals in your landscape is a crucial aspect of sustainable landscaping. By opting for organic fertilizers, avoiding pesticides, and using natural pest control methods, you can create a safe and healthy environment for both humans and wildlife.
Opting for organic fertilizers
Using organic fertilizers, such as compost or well-rotted manure, provides a slow-release source of nutrients to plants. These natural fertilizers enrich the soil, improve its structure, and promote healthy plant growth without introducing harmful chemicals to the environment. Consider creating your compost pile or purchasing organic fertilizers to minimize chemical inputs.
Avoiding pesticides
Pesticides not only harm beneficial insects and wildlife but can also have adverse effects on human health. Instead of relying on chemical pesticides, embrace natural pest control methods such as companion planting, encouraging beneficial insects, or using physical barriers and traps. Regularly monitor your plants for signs of pests or diseases and address any issues promptly.
Using natural pest control methods
Natural pest control methods, such as companion planting and encouraging beneficial insects, can help keep pest populations in check without the need for chemical interventions. Planting insect-repellent herbs like basil or lavender, or attracting beneficial insects like ladybugs and praying mantises, can help control pests naturally. Additionally, using physical barriers like nets or row covers can protect plants from pest damage.

This image is property of www.bhg.com.
Addressing Climate Challenges
With the ongoing challenges posed by climate change, it is crucial to design landscapes that can withstand and adapt to changing conditions. By creating microclimates, selecting plants for resilience, and considering climate change projections, you can address climate challenges in your sustainable landscape.
Creating microclimates
Creating microclimates within your landscape involves manipulating environmental factors such as sunlight, wind, and moisture to suit specific plant requirements. By strategically placing windbreaks or using reflective surfaces, you can shield vulnerable plants from strong winds or excessive heat. Additionally, consider creating shaded areas or installing misting systems to provide relief during hot and dry periods.
Selecting plants for resilience
Selecting plants that are resilient to climate challenges, such as drought, heat, or extreme cold, is essential for long-term sustainability. Choose plant species that have a proven track record of withstanding local climatic conditions. Consider consulting local plant nurseries or gardening experts who can provide insights on the best plant selections for your region.
Considering climate change projections
When designing a sustainable landscape, it is important to consider future climate change projections. Take into account factors such as increased temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, or the potential for extreme weather events. By selecting plants and implementing strategies that are adaptable and resilient to these projected changes, you can future-proof your landscape.
Engaging the Community
Engaging the community and fostering a sense of environmental responsibility is key to creating a sustainable landscape. By educating neighbors, participating in local initiatives, and sharing resources and knowledge, you can inspire others to join the movement towards sustainability.
Educating neighbors
Take the opportunity to educate your neighbors about the benefits of sustainable landscaping. Share information about water conservation, native plants, and wildlife-friendly practices. Organize workshops or garden tours to showcase your sustainable landscape and inspire others to adopt similar practices. By raising awareness and sharing knowledge, you can create a ripple effect of positive change within your community.
Participating in local initiatives
Get involved in local initiatives and organizations that promote sustainable landscaping and environmental stewardship. Join community gardening groups, volunteer for tree-planting events, or participate in neighborhood cleanup activities. By actively engaging in these initiatives, you not only contribute to the overall sustainability of your community but also foster a sense of community spirit.
Sharing resources and knowledge
Share your resources and knowledge with others who are interested in creating sustainable landscapes. Offer plants or cuttings from your garden, provide gardening tips and advice, or create online platforms where like-minded individuals can connect and share their experiences. By building a community of individuals passionate about sustainable landscaping, you can collectively make a significant impact on the environment.
In conclusion, designing a sustainable landscape involves careful analysis, thoughtful planning, and the implementation of eco-friendly practices. Whether you have a small space or a large yard, you can make a positive impact by choosing native plants, conserving water, promoting biodiversity, managing soil health, reducing maintenance needs, enhancing energy efficiency, minimizing chemical inputs, addressing climate challenges, and engaging your community. By following these principles and incorporating sustainable practices into your landscaping, you can create a beautiful, resilient, and environmentally-friendly outdoor space.