In this article, we will be discussing the transition to renewable energy and how it can help reduce emissions. We will explore the power of renewables and how they can play a crucial role in our fight against climate change. By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of why transitioning to renewable energy is important and the various benefits it can bring to our environment and society. So let’s get started on this journey towards a greener and sustainable future together. Renewable Energy Transition: Zero Emissions and the Power of Renewables

This image is property of rmi.org.
Understanding Renewable Energy
Renewable energy refers to energy sources that are continuously replenished and do not deplete natural resources. These sources, such as solar power, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, biomass, and bioenergy, play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
Importance of Renewable Energy Transition
The transition to renewable energy is of utmost importance in addressing the global climate crisis and transitioning towards a sustainable future. The reliance on fossil fuels for energy production has contributed significantly to the rise in greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to renewable energy sources, we can reduce our carbon footprint and protect the environment for future generations.

This image is property of www2.deloitte.com.
Benefits of Renewable Energy Transition
The transition to renewable energy offers numerous benefits, both environmental and economic. Firstly, it helps combat climate change by reducing emissions and stabilizing the Earth’s temperature. This transition also provides energy security, as renewable energy sources are infinite and do not rely on imported fossil fuels. Additionally, transitioning to renewables promotes job creation and economic growth, fostering a green economy.
Zero Emissions and Climate Change
It is essential to understand the impact fossil fuels have on climate change. The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas releases greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global warming and climate-related disasters such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and loss of biodiversity.

This image is property of www.mckinsey.com.
Role of Renewable Energy in Reducing Emissions
Renewable energy sources play a crucial role in reducing emissions, as they produce electricity without significant CO2 emissions. Solar power harnesses the sun’s energy through photovoltaic (PV) panels, while wind energy utilizes wind turbines to convert wind into electricity. Hydropower, geothermal energy, biomass, and bioenergy also contribute to the reduction of emissions by providing clean and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels.
Transitioning to a Zero Emissions Future
To achieve a zero-emissions future, it is necessary to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. This transition involves investing in renewable energy technologies, improving their efficiency, and integrating them into the existing power grid. It requires collaborative efforts from governments, businesses, and individuals to drive the transition towards a sustainable and climate-friendly energy system.
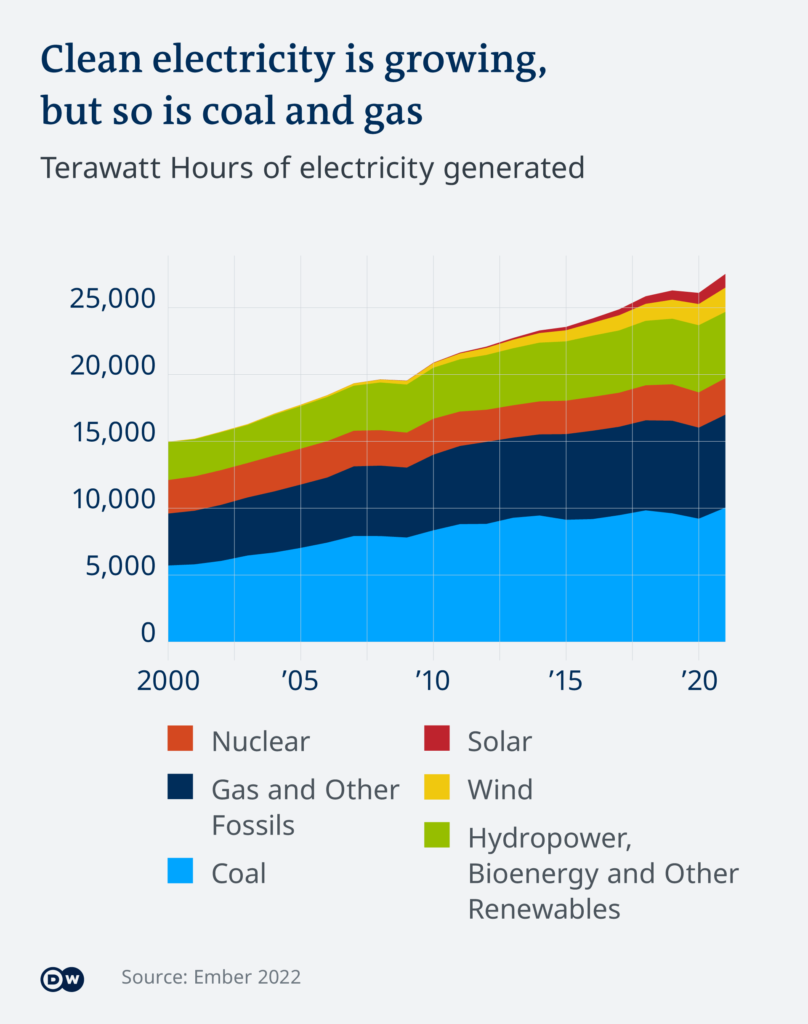
This image is property of static.dw.com.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
There are several types of renewable energy sources that can be harnessed to meet our energy needs:
Solar Power
Solar power is derived from the sun’s energy and converted into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrated solar power (CSP) systems. It is a widely available and abundant source of energy, making it a promising solution for sustainable power generation.
Wind Energy
Wind energy is harnessed by wind turbines that convert kinetic energy from the wind into electricity. Wind power is a versatile and cost-effective source of energy, capable of powering both small-scale and large-scale electricity grids.
Hydropower
Hydropower uses the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. It is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources, accounting for a significant portion of global renewable energy capacity.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy harnesses the natural heat from beneath the Earth’s surface to generate electricity. It is a reliable and sustainable source of energy, particularly useful in regions with geothermal activity.
Biomass and Bioenergy
Biomass refers to organic matter derived from plants and animal waste, which can be converted into bioenergy through various processes. Bioenergy includes biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, as well as direct combustion of biomass for heat and power generation.
Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies
Continuous advancements in renewable energy technologies have significantly improved the efficiency and effectiveness of harnessing renewable energy sources. Some notable advancements include:
Solar Panel Efficiency Improvements
Scientists and engineers have made substantial progress in improving the efficiency of solar panels, allowing them to convert a higher percentage of sunlight into usable electricity. This breakthrough has helped make solar power more accessible and cost-effective.
Wind Turbine Innovations
Wind turbine technology has evolved over the years, leading to the development of larger, more efficient turbines that can generate higher amounts of clean energy. Innovations such as floating offshore wind farms and vertical axis wind turbines are pushing the boundaries of wind energy generation.
Hydroelectric Power Enhancements
Advancements in hydropower technology include smaller-scale turbines that can be installed in rivers and streams, making hydropower more accessible in remote areas. Additionally, improvements in dam design and operating techniques have increased the efficiency and environmental sustainability of hydropower.
Geothermal Heat Pump Systems
Geothermal heat pump systems utilize the constant temperature of the Earth to heat and cool buildings efficiently. Advances in heat pump technology have made geothermal systems more efficient, reducing energy consumption and lowering carbon emissions.
Biofuel Production Techniques
Researchers have been working on developing advanced biofuel production techniques, such as cellulosic ethanol and algae-based biofuels. These innovations aim to increase the availability and sustainability of biofuels, providing a greener alternative to fossil fuels.
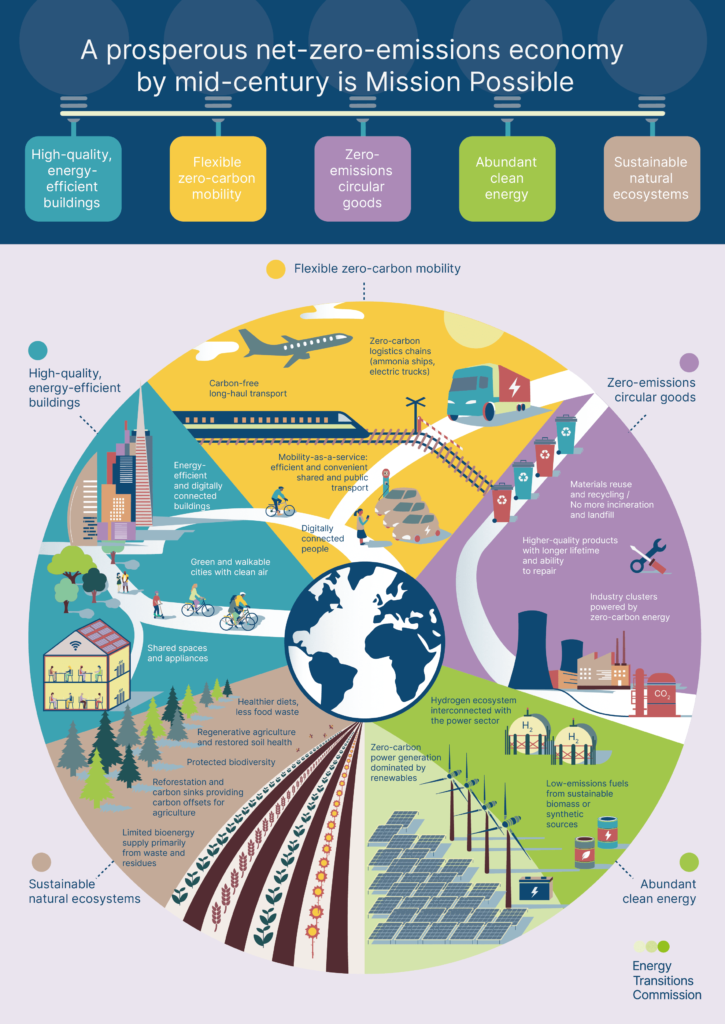
This image is property of assets.weforum.org.
Integration of Renewables into the Power Grid
Integrating renewable energy sources into the existing power grid poses various challenges and requires innovative solutions. Some key considerations include:
Challenges and Solutions
Intermittency, or the fluctuating nature of renewable energy sources, poses challenges for grid stability. To address this, grid operators use advanced forecasting techniques and energy management systems to optimize the integration of renewables and balance supply and demand.
Smart Grids and Energy Storage
Smart grids enable the real-time monitoring and control of electricity supply and demand, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped storage, play a crucial role in storing excess renewable energy for later use, ensuring a steady and reliable power supply.
Demand Response Strategies
Demand response strategies involve incentivizing consumers to shift their electricity usage to align with the availability of renewable energy. By adjusting energy consumption patterns, demand response helps maximize the utilization of renewable energy and optimize grid performance.
Renewable Energy Policies and Incentives
Governments around the world have implemented various policies and incentives to encourage the adoption of renewable energy. Some notable examples include:
Feed-in Tariffs
Feed-in tariffs guarantee renewable energy producers a premium price for the electricity they generate. This incentivizes private individuals and businesses to invest in renewable energy projects and sell excess electricity back to the grid.
Renewable Portfolio Standards
Renewable portfolio standards require utilities to obtain a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources. These standards promote the development and integration of renewable energy into the overall energy mix.
Tax Credits
Tax credits provide financial incentives to individuals and businesses that invest in renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines. These credits help offset the upfront costs of installation and encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
Green Certificates
Green certificates, also known as Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) or tradable green certificates, provide proof that a certain amount of electricity has been generated from renewable sources. Certificates can be bought and sold, providing an additional revenue stream for renewable energy producers.
Renewable Energy Investments and Economics
The cost of renewable energy technologies has significantly decreased in recent years, making them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. Some key considerations regarding renewable energy investments and economics include:
Cost Reductions and Competitive Pricing
Advancements in technology, economies of scale, and supportive policies have contributed to cost reductions in renewable energy production. Solar and wind energy, in particular, have become cost-competitive with conventional energy sources in many regions.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
The renewable energy sector has the potential to create a significant number of jobs and foster economic growth. Investments in renewable energy projects stimulate local economies, creating employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, operations, and maintenance.
Financial Benefits for Businesses and Individuals
By investing in renewable energy systems, businesses and individuals can reduce their electricity costs and achieve energy independence. Renewable energy installations can also generate income through selling excess electricity back to the grid or through feed-in tariffs.
Global Efforts towards Renewable Energy Transition
The global community has made significant efforts to transition to renewable energy and combat climate change. Some notable initiatives include:
International Agreements and Commitments
International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Under this agreement, countries have committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy deployment.
National Renewable Energy Targets
Many countries have set ambitious renewable energy targets to drive the transition towards clean energy. These targets provide a framework for policymakers and investors, fostering the development of renewable energy infrastructure.
Government Support and Funding
Governments worldwide are providing support and funding for renewable energy projects through grants, subsidies, and research and development initiatives. These incentives encourage private investment and accelerate the deployment of renewable energy technologies.
Challenges and Barriers to Renewable Energy Transition
While the transition to renewable energy offers numerous benefits, there are several challenges and barriers that need to be addressed:
Intermittency and Storage
Intermittent energy production from renewable sources, such as solar and wind, requires effective energy storage solutions to ensure a continuous power supply. Developing affordable and efficient energy storage technologies is critical to overcoming this challenge.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Integrating renewable energy into existing energy infrastructure requires upgrades and modifications to the grid. This can be a complex process, requiring collaboration between grid operators, utilities, and renewable energy project developers.
Political and Regulatory Obstacles
Political and regulatory obstacles, such as inconsistent policies and lack of political will, can slow down the transition to renewable energy. It is essential for policymakers to provide stable and supportive policy environments to facilitate investment and innovation in the renewable energy sector.
Public Perception and Awareness
Public perception and awareness of renewable energy play a significant role in driving its adoption. Educating the public about the benefits and potential of renewable energy is crucial for overcoming misconceptions and garnering support for the transition.
Technological Innovations and Future Trends
The continuous evolution of renewable energy technologies is leading to exciting innovations and future trends. Some notable examples include:
Emerging Energy Storage Solutions
Researchers are actively working on developing advanced energy storage solutions, such as flow batteries, compressed air energy storage, and hydrogen storage. These innovations aim to address the challenge of intermittent renewable energy production and provide reliable energy storage options.
Advancements in Grid Integration
Improvements in grid integration technologies facilitate the seamless integration of various renewable energy sources and optimize grid performance. This includes solutions such as virtual power plants, demand-side management, and enhanced grid automation.
Use of Artificial Intelligence in Renewables
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being increasingly utilized in renewable energy systems to optimize energy production and consumption. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, allowing for more efficient control and operation of renewable energy systems.
Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems
Hybrid renewable energy systems combine multiple renewable energy sources to provide a more reliable and consistent power supply. By diversifying energy sources, hybrid systems can overcome the intermittency issue and ensure a stable energy supply.
Case Studies of Successful Renewable Energy Transition
Several countries and regions have successfully implemented renewable energy transition strategies. Some notable case studies include:
Germany’s Energiewende
Germany’s Energiewende, or “energy transition,” is a comprehensive plan to transition from nuclear and fossil fuel energy to a renewable energy-based system. The country has set ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment and has heavily invested in solar and wind power. Germany is now a global leader in renewable energy capacity.
Iceland’s Geothermal Transformation
Iceland has successfully harnessed its abundant geothermal resources to meet its energy needs. Geothermal power provides a significant portion of the country’s electricity and heating requirements, reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Costa Rica’s 100% Renewable Power
Costa Rica aims to achieve 100% renewable electricity generation by 2030. The country has made significant progress in diversifying its energy mix, utilizing hydropower, wind energy, and geothermal energy. As a result, Costa Rica has already seen prolonged periods of 100% renewable energy generation.
California’s Clean Energy Transition
California has set ambitious renewable energy goals, with a target of sourcing 100% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2045. The state has implemented various policies and incentives to drive the adoption of solar power, wind energy, and energy storage technologies.
Environmental and Health Benefits of Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy sources offers significant environmental and health benefits:
Reduced Air Pollution
Renewable energy sources produce little to no air pollutants compared to fossil fuels. By substituting fossil fuel-generated electricity with renewable energy, we can reduce air pollution and improve air quality, leading to better respiratory health and lower rates of respiratory diseases.
Preservation of Natural Resources
Renewable energy sources do not deplete natural resources as they rely on constantly replenished sources, such as sunlight, wind, and water. This preserves natural resources, minimizes ecological disruption, and reduces the need for resource extraction and transportation.
Positive Impact on Human Health
Renewable energy’s clean and sustainable nature has a positive impact on human health. By reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy mitigates the effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events and the spread of vector-borne diseases.
Mitigating Environmental Disasters
Renewable energy transition plays a crucial role in mitigating the impacts of environmental disasters, such as oil spills and nuclear accidents. By reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and nuclear power, we can minimize the risk of catastrophic events and their long-term environmental consequences.
Balancing Renewable Energy with Energy Demand
Ensuring a balance between renewable energy generation and energy demand is essential for a sustainable energy future:
Flexible Power Systems
Flexibility in power systems allows for the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources. Flexible power systems can quickly adjust power production and consumption based on the availability of renewable energy, optimizing the use of clean energy.
Energy Efficiency Measures
Promoting energy efficiency is a crucial component of balancing energy demand with renewable energy generation. By reducing energy consumption through energy-efficient technologies and practices, we can minimize the need for additional energy generation.
Interconnected Energy Networks
Interconnecting energy networks, both within and across regions, helps balance renewable energy generation and demand. Interconnected grids enable the sharing and trading of renewable energy, enhancing energy security and stability.
Conclusion
The transition to renewable energy is vital for addressing climate change, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and creating a sustainable future. By harnessing the power of renewable energy sources, we can move towards a zero-emissions world and mitigate the detrimental effects of fossil fuel dependence. Collaborative efforts from governments, businesses, and individuals are essential to drive the renewable energy transition and secure a cleaner and greener energy future for generations to come.