Welcome! In this article, we will discuss the topic of sustainable landscapes and how you can make a positive impact on the environment. You’ll learn about the benefits of using zero emission tools and how they can help you maintain your landscape without harming the planet. By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of sustainable landscaping practices and the tools available to make it easier for you to go green. Let’s get started!

This image is property of image.cnbcfm.com.
What are Sustainable Landscapes?
Sustainable landscapes are designed and managed in a way that minimizes negative environmental impacts while promoting positive ecological and social outcomes. These landscapes take into consideration factors such as water conservation, energy efficiency, biodiversity conservation, and the use of environmentally friendly materials and practices. The goal of sustainable landscapes is to create harmonious and resilient outdoor spaces that provide multiple benefits to both humans and the environment. By adopting sustainable practices in landscaping, we can contribute to the conservation of natural resources, reduce pollution, and enhance the overall quality of life for ourselves and future generations.
Definition of Sustainable Landscapes
Sustainable landscapes can be defined as outdoor spaces that are carefully planned, designed, and managed to achieve environmental, economic, and social sustainability goals. These goals encompass a variety of aspects, including water conservation, energy efficiency, waste reduction, carbon neutrality, biodiversity conservation, and the promotion of human health and well-being.
A sustainable landscape aims to minimize the negative impacts on the environment by using resources efficiently, reducing waste generation, and adopting eco-friendly practices. This includes the use of native plants, which require less water, nutrients, and pesticides, and are better adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. Sustainable landscapes also promote the preservation and restoration of natural habitats, which provide food, shelter, and breeding grounds for wildlife.
Importance of Sustainable Landscapes
Sustainable landscapes play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental challenges we face today, such as climate change, habitat loss, water scarcity, and pollution. By adopting sustainable practices in landscaping, we can make a significant positive impact on the environment and create a healthier and more sustainable future.
One of the key benefits of sustainable landscapes is water conservation. By implementing efficient irrigation systems, capturing and reusing rainwater, and using drought-tolerant plants, we can significantly reduce water consumption in outdoor spaces. This not only helps to conserve a precious natural resource but also reduces the strain on water supply systems and protects sensitive aquatic ecosystems.
Sustainable landscapes also contribute to energy efficiency. By strategically planting trees and shrubs to provide shade and windbreaks, and by using energy-efficient outdoor lighting systems, we can reduce the need for artificial cooling and lighting, which in turn reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, sustainable landscapes enhance biodiversity and provide habitat for local wildlife. By planting native species and creating diverse ecosystems, we can attract pollinators, birds, and beneficial insects, which play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems. This promotes biodiversity conservation and contributes to the overall health and resilience of our natural environment.
In addition to the environmental benefits, sustainable landscapes also provide social and economic advantages. They create beautiful and functional outdoor spaces for recreational activities, improve air quality, and increase property values. Moreover, sustainable landscaping practices can reduce maintenance costs, as native plants require less water, fertilizer, and pesticides compared to non-native species.
Zero Emission Tools for Sustainable Landscapes
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for zero emission tools in landscaping. These tools are powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar and electricity, and produce no harmful emissions or pollutants during operation. Zero emission tools offer a cleaner, quieter, and more sustainable alternative to traditional gas-powered equipment, making them an ideal choice for sustainable landscapes.
Overview of Zero Emission Tools
Zero emission tools encompass a wide range of equipment used for various landscaping tasks. These tools include solar-powered equipment, electric machinery, battery-powered tools, sustainable irrigation systems, green waste management practices, plant selection strategies, permeable paving solutions, and rainwater harvesting techniques. Each of these tools offers unique benefits and contributes to the overall sustainability of a landscape.
Benefits of Zero Emission Tools
Zero emission tools offer several benefits compared to traditional gas-powered equipment. Firstly, they significantly reduce air and noise pollution. Gas-powered equipment emits harmful pollutants, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds, which contribute to air pollution and negatively impact human health. Zero emission tools produce no exhaust emissions, making them cleaner and safer for both the environment and our well-being.
Secondly, zero emission tools are more energy-efficient. Solar-powered equipment harnesses the energy of the sun, which is a renewable and abundant source of power. Electric machinery requires less energy to operate compared to gas-powered machinery, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Battery-powered tools offer the advantage of being rechargeable, eliminating the need for disposable batteries and reducing waste.
Lastly, zero emission tools are cost-effective in the long run. Although the initial investment may be higher compared to gas-powered equipment, the savings in fuel costs and maintenance expenses make them a more economical choice over time. In addition, some governments and utilities offer incentives and subsidies for the purchase and use of zero emission tools, further reducing the costs of adoption.

This image is property of www.bhg.com.
1. Solar-Powered Equipment
Solar-powered equipment utilizes solar energy to power various landscaping tools and equipment. These tools are equipped with photovoltaic panels that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which is then used to operate the equipment. Solar-powered equipment offers a range of benefits for sustainable landscapes.
Advantages of Solar-Powered Equipment
One of the primary advantages of solar-powered equipment is its environmental friendliness. By harnessing the clean and renewable energy of the sun, these tools produce no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution during operation. This helps to reduce the carbon footprint and minimize the impact on climate change.
Solar-powered equipment is also cost-effective in the long run. While the initial investment may be higher compared to traditional tools, the savings in fuel costs and maintenance expenses make them a more economical choice over time. Once the equipment is installed, the energy from the sun is free, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering operational costs.
In addition, solar-powered equipment is quiet and emits less noise compared to gas-powered equipment. This makes it ideal for use in residential areas and noise-sensitive environments, such as schools, parks, and hospitals. The quiet operation also creates a more peaceful and enjoyable outdoor experience for users.
Types of Solar-Powered Equipment
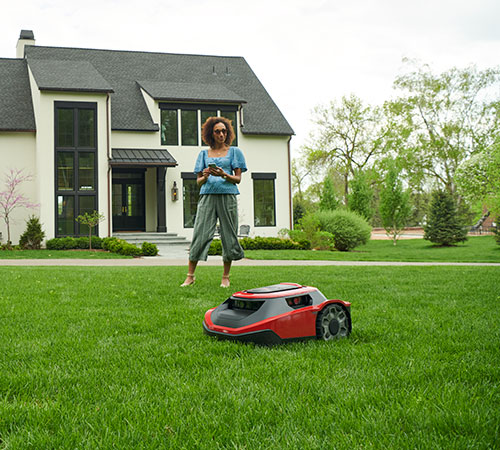
There are various types of solar-powered equipment available for sustainable landscapes. These include solar-powered garden lights, solar-powered water pumps and fountains, solar-powered ventilation and cooling systems, and even solar-powered robotic mowers.
Solar-powered garden lights are a popular choice for outdoor lighting in sustainable landscapes. These lights use solar panels to charge built-in batteries during the day, which then power the LED lights at night. Solar-powered garden lights are easy to install, require no wiring, and come in a variety of designs and styles to suit different preferences.
Solar-powered water pumps and fountains are another useful addition to sustainable landscapes. These systems use solar energy to power water pumps and create beautiful water features. Solar-powered water pumps can be used in ponds, waterfalls, and irrigation systems, providing a renewable and environmentally friendly solution for water circulation and distribution.
For those looking to improve ventilation and cooling in outdoor spaces, solar-powered ventilation and cooling systems are a great option. These systems use solar energy to power fans and air conditioning units, creating a comfortable and cool environment without relying on electricity from the grid.
Lastly, solar-powered robotic mowers provide an innovative and sustainable solution for lawn maintenance. These robotic mowers are equipped with solar panels that charge the batteries during the day, enabling them to mow the lawn autonomously without any emissions or noise. Solar-powered robotic mowers ensure a well-manicured lawn while minimizing the impact on the environment.
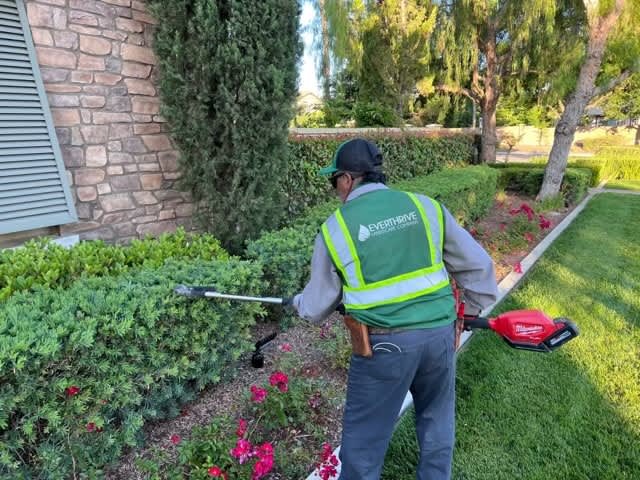
2. Electric Machinery
Electric machinery offers an alternative to gas-powered machinery in landscaping. These tools are powered by electricity, either through a corded connection or a battery. Electric machinery provides several advantages in terms of sustainability, efficiency, and noise reduction.
Advancements in Electric Machinery
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in electric machinery, making them more powerful, durable, and versatile. Electric lawn mowers, chainsaws, hedge trimmers, and leaf blowers are now available in electric versions that can rival their gas-powered counterparts in performance and efficiency.
Electric machinery is more energy-efficient compared to gas-powered machinery. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy with high efficiency, resulting in less energy wastage and lower operational costs. Electric tools also do not require fuel, eliminating the need for purchasing and storing fossil fuels.
Furthermore, electric machinery is significantly quieter compared to gas-powered machinery. The absence of a noisy combustion engine makes electric tools more suitable for use in noise-sensitive environments, such as residential areas or parks. Electric machinery ensures a peaceful and pleasant outdoor experience for both users and nearby residents.
Types of Electric Machinery
There is a wide range of electric machinery available for sustainable landscapes. These include electric lawn mowers, electric chainsaws, electric hedge trimmers, electric leaf blowers, and electric edgers.
Electric lawn mowers provide a sustainable and efficient solution for grass cutting. These mowers are available in corded and cordless versions. Corded electric lawn mowers require a power cord and a nearby electrical outlet for operation. Cordless electric lawn mowers are powered by rechargeable batteries and offer more mobility and flexibility. Electric lawn mowers are quieter, produce no emissions, and require less maintenance compared to gas-powered mowers.
Electric chainsaws are a safer and more sustainable alternative to gas-powered chainsaws. These tools are ideal for pruning, cutting small trees, and firewood preparation. Electric chainsaws are lightweight, easy to operate, emit no exhaust fumes, and produce less noise compared to their gas-powered counterparts. They are also maintenance-friendly, as they do not require oil changes or spark plug replacements.
Electric hedge trimmers are used for shaping and pruning hedges, shrubs, and bushes. These tools are lightweight, maneuverable, and produce less noise compared to gas-powered hedge trimmers. Electric hedge trimmers are also more compact and emission-free, making them a suitable choice for small gardens and noise-sensitive areas.
Electric leaf blowers provide a sustainable solution for leaf and debris removal. These tools effectively blow leaves and debris off driveways, sidewalks, and lawns, helping to maintain a clean and tidy outdoor space. Electric leaf blowers are quieter, lighter, and produce no emissions compared to gas-powered leaf blowers. They are also easier to start, require less maintenance, and offer more control over the airflow.
Electric edgers are used to create clean and defined edges along driveways, sidewalks, and garden beds. These tools are lightweight, easy to maneuver, and produce less noise compared to gas-powered edgers. Electric edgers are more environmentally friendly, as they do not emit exhaust fumes or require gasoline.
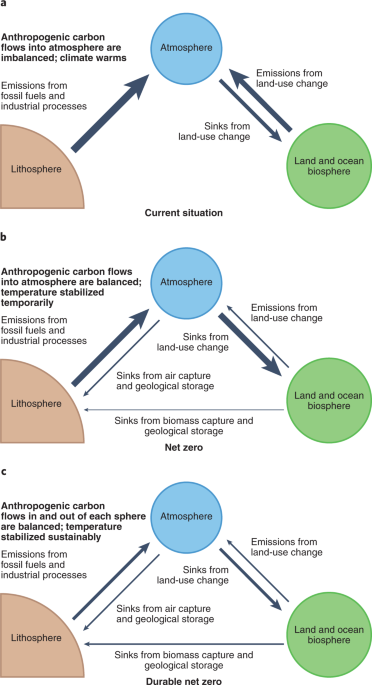
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
3. Battery-Powered Tools
Battery-powered tools offer a convenient and sustainable alternative for landscaping tasks. These tools are powered by rechargeable batteries, which provide the necessary energy for operation. Battery-powered tools offer several benefits in terms of portability, ease of use, and reduced environmental impact.
Benefits of Battery-Powered Tools
One of the primary benefits of battery-powered tools is their portability and flexibility. Since these tools are not corded, they offer greater mobility and maneuverability, allowing users to move around freely without the constraints of a power cord. This makes battery-powered tools ideal for large outdoor spaces or areas without a nearby power source.
Battery-powered tools are also easy to use, as they eliminate the need for pulling cords or mixing fuel. With just a simple press of a button, battery-powered tools can be activated and ready to use. This makes them a convenient choice for homeowners and landscapers of all skill levels.
Another advantage of battery-powered tools is their reduced impact on the environment. By using rechargeable batteries, these tools eliminate the need for disposable batteries, reducing waste generation and minimizing the environmental footprint. Additionally, battery-powered tools produce no exhaust emissions, improving air quality and promoting a cleaner and healthier outdoor environment.
Types of Battery-Powered Tools
There is a wide variety of battery-powered tools available for sustainable landscapes. These include battery-powered lawn mowers, battery-powered chainsaws, battery-powered hedge trimmers, battery-powered leaf blowers, and battery-powered string trimmers.
Battery-powered lawn mowers offer a convenient and environmentally friendly solution for grass cutting. These mowers are equipped with rechargeable batteries, providing the necessary power for lawn maintenance. Battery-powered lawn mowers are lightweight, easy to maneuver, and produce less noise compared to gas-powered mowers. They are also emission-free, making them a sustainable choice for maintaining a well-manicured lawn.
Battery-powered chainsaws are a quiet and efficient alternative to gas-powered chainsaws. These tools are suitable for small to medium-sized cutting tasks, such as pruning, limbing, and firewood preparation. Battery-powered chainsaws are lightweight, easy to handle, and produce no emissions. They are also easier to start compared to gas-powered chainsaws, as they do not require pulling cords or mixing fuel.
Battery-powered hedge trimmers are used for shaping and pruning hedges, shrubs, and bushes. These tools offer the advantage of being cordless, providing greater mobility and flexibility. Battery-powered hedge trimmers are lightweight, easy to use, and produce less noise compared to gas-powered hedge trimmers. They are also emission-free, making them a sustainable choice for maintaining well-trimmed hedges.
Battery-powered leaf blowers provide a clean and efficient solution for leaf and debris removal. These tools effectively blow leaves and debris off driveways, sidewalks, and lawns, helping to maintain a tidy outdoor space. Battery-powered leaf blowers are lightweight, easy to operate, and produce less noise compared to gas-powered leaf blowers. They are also emission-free and require minimal maintenance.
Battery-powered string trimmers, also known as weed eaters or weed whackers, are used to trim grass and weeds in hard-to-reach areas. These tools offer a cordless and convenient solution for edging and trimming tasks. Battery-powered string trimmers are lightweight, easy to handle, and produce less noise compared to gas-powered trimmers. They are also emission-free, making them an eco-friendly choice for maintaining a neat and tidy landscape.
4. Sustainable Irrigation Systems
Sustainable irrigation systems play a crucial role in water conservation and efficient landscape management. These systems are designed to distribute water in a precise, controlled, and efficient manner, ensuring that plants receive the necessary water without wastage. Sustainable irrigation techniques and smart controllers are key components of sustainable landscapes.
Efficient Irrigation Techniques
Efficient irrigation techniques aim to minimize water consumption and reduce water waste in landscapes. Some of the most common efficient irrigation techniques include drip irrigation, micro-sprinklers, and rainwater harvesting.
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient technique that delivers water directly to the plant’s root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff. In a drip irrigation system, water is distributed through a network of small tubes with emitters, which release water slowly and directly onto the soil. This ensures that water reaches the plants’ roots, where it is needed the most. Drip irrigation reduces water wastage, promotes plant health, and prevents weed growth by delivering water only to the desired plants.
Micro-sprinklers are another effective irrigation technique for sustainable landscapes. These systems use low-volume sprinklers to distribute water evenly across the landscape. Micro-sprinklers release small droplets of water that are less prone to evaporation and wind drift, ensuring efficient water distribution. Micro-sprinklers can be adjusted to deliver water only to specific areas, minimizing water waste and improving water use efficiency.
Rainwater harvesting is an essential component of sustainable irrigation systems. It involves collecting and storing rainwater for later use in irrigation. Rainwater can be collected from roofs, gutters, or rain barrels, and stored in tanks or cisterns. Rainwater harvesting reduces the reliance on freshwater sources, conserves water resources, and provides a sustainable water supply for plants during dry periods.
Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers are advanced technologies that automate and optimize irrigation systems. These controllers use real-time weather data, soil moisture sensors, and plant water requirements to adjust irrigation schedules and deliver water efficiently.
Weather-based smart controllers use data from local weather stations to adjust irrigation schedules based on current and forecasted weather conditions. By considering factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and rainfall, these controllers ensure that irrigation is only applied when necessary, reducing water waste and preventing overwatering.
Soil moisture sensors are another important component of smart irrigation systems. These sensors monitor the moisture levels in the soil and transmit the data to the controller. Based on the soil moisture readings, the controller determines when irrigation is needed and adjusts the watering schedule accordingly. Soil moisture sensors prevent overwatering and ensure that plants receive the appropriate amount of water at the right time.
Plant water requirements are also taken into account by smart irrigation controllers. These controllers are programmed with the specific water needs of different plant species and adjust the irrigation schedule accordingly. By tailoring irrigation to the specific needs of plants, smart controllers optimize water use, minimize water waste, and promote plant health and growth.
Smart irrigation controllers can be integrated with mobile apps and online platforms, allowing users to monitor and control their irrigation systems remotely. This provides convenience and flexibility, as users can adjust irrigation schedules and settings from anywhere using their smartphones or computers.
This image is property of cdn2.toro.com.
5. Green Waste Management Practices
Green waste management practices are essential for maintaining a sustainable landscape. These practices involve the proper handling and disposal of organic waste materials, such as grass clippings, leaves, branches, and other garden debris. By adopting green waste management practices, we can reduce waste generation, promote recycling and composting, and create valuable resources for our landscapes.
Composting
Composting is a natural process that decomposes organic materials and transforms them into nutrient-rich compost. Composting green waste not only reduces the amount of waste going to landfills but also provides a valuable resource for improving soil health and fertility.
To compost green waste, start by collecting and accumulating organic materials such as grass clippings, leaves, small branches, and kitchen scraps. These materials should be placed in a compost bin or heap, along with a mix of dry carbon-rich materials, such as dried leaves, newspaper, or cardboard. The compost pile should be regularly turned or mixed to ensure proper aeration and decomposition.
Over time, the organic materials will break down into compost, which can be used as a natural fertilizer and soil amendment in the landscape. Compost enriches the soil, improves its structure, and enhances its water-holding capacity. By using compost in the landscape, we can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and enhance the health and vitality of plants.
Mulching
Mulching is another important green waste management practice that helps to conserve water, control weeds, and improve soil health. Mulch is a layer of organic or inorganic material spread on the soil surface around plants. Mulch can be made from a variety of materials, including wood chips, straw, grass clippings, leaves, or shredded bark.
Mulch helps to retain soil moisture by reducing evaporation and preventing weed growth. It acts as a protective barrier, keeping the soil temperature more stable and reducing the need for frequent watering. Mulch also improves soil fertility as it breaks down over time, adding organic matter and nutrients to the soil.
To mulch the landscape, spread a layer of mulch around the base of plants, leaving a small gap around the stem to prevent rot. The thickness of the mulch layer should be around 2-4 inches, depending on the type of material used. Mulch should be replenished periodically to maintain its effectiveness and aesthetic appeal.
By mulching the landscape, we can reduce water usage, minimize weed competition, improve plant health, and enhance the overall appearance of the outdoor space. Mulching is a sustainable practice that adds value to the landscape while reducing waste and promoting resource conservation.
Recycling
Recycling is an essential aspect of green waste management in sustainable landscapes. Recycling involves the collection, separation, and processing of materials to create new products. By recycling waste materials, we can conserve natural resources, reduce pollution, and minimize the demand for virgin materials.
In sustainable landscapes, recycling can involve the proper disposal of non-organic waste materials, such as plastic containers, metal cans, glass bottles, and cardboard boxes. These materials should be collected separately and sent to recycling facilities or placed in designated recycling bins.
Additionally, recycling can also involve the use of recycled materials in landscaping projects. Recycled materials, such as recycled wood, plastic lumber, or recycled glass, can be used for various applications, including decking, fencing, pathways, or garden accessories. Using recycled materials reduces the need for virgin materials, saves energy, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
It is important to educate and inform the community about the importance of recycling and provide convenient recycling options in public spaces, parks, and residential areas. By promoting recycling in sustainable landscapes, we can create a more circular and sustainable economy while reducing waste and preserving natural resources.
6. Plant Selection for Sustainable Landscapes
Plant selection plays a crucial role in creating sustainable landscapes. By choosing the right plants for the right locations, we can minimize water consumption, reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers, support local ecosystems, and enhance the overall beauty and functionality of the outdoor space. Native plants and drought-tolerant plants are key considerations in plant selection for sustainable landscapes.
Native Plants and their Benefits
Native plants are species that naturally occur in a specific region or ecosystem. They are adapted to the local climate, soil conditions, and wildlife interactions. Choosing native plants for sustainable landscapes offers several benefits.
Native plants require less water compared to non-native species. They have evolved to survive in the local climate and are adapted to the amount of rainfall and soil moisture available. Native plants have deep root systems that can access water deep in the soil, making them more drought-tolerant and water-efficient.
Native plants also provide important habitat and food sources for local wildlife. They support pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds, by providing nectar, pollen, and shelter. Native plants attract beneficial insects that control pests, creating a healthy and balanced ecosystem.
In addition, native plants are generally low-maintenance and disease-resistant. They are adapted to the local soil, pests, and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and fertilizers. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also lowers maintenance costs and effort.
By incorporating native plants in sustainable landscapes, we can conserve water, support biodiversity, and create beautiful and resilient outdoor spaces that are well-adapted to the local climate and environment.
Drought-Tolerant Plants
In regions with limited water resources or frequent drought conditions, drought-tolerant plants are a valuable addition to sustainable landscapes. These plants are adapted to survive with minimal irrigation and are resistant to drought stress. They have unique characteristics that enable them to withstand hot and dry conditions, such as deep root systems, succulent leaves, or water storage tissues.
Drought-tolerant plants come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors, offering a wide selection for landscape design. Examples of drought-tolerant plants include agaves, yuccas, succulents, lavender, sage, lantana, and ornamental grasses. These plants provide vibrant colors, interesting textures, and architectural elements that enhance the overall aesthetics and appeal of the landscape.
By incorporating drought-tolerant plants in sustainable landscapes, we can conserve water, reduce irrigation needs, and create visually stunning and resilient outdoor spaces that thrive even in challenging climatic conditions.
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
7. Permeable Paving Solutions
Permeable paving solutions are an innovative and sustainable alternative to traditional impervious pavement in landscapes. Permeable pavements allow water to infiltrate into the ground, reducing stormwater runoff, preventing flooding, and promoting groundwater recharge. They offer several benefits in terms of water management, pollution reduction, and temperature moderation.
Benefits of Permeable Pavement
One of the primary benefits of permeable pavement is its ability to manage stormwater runoff. Traditional impervious pavement, such as concrete or asphalt, prevents rainwater from infiltrating into the ground, leading to increased runoff and water pollution. Permeable pavements, on the other hand, allow water to permeate through the surface and into the underlying soil. This helps to reduce stormwater runoff, control erosion, and prevent flooding in urban areas.
Permeable pavements also play a crucial role in water quality improvement. As water infiltrates through the pavement, it undergoes natural filtration, which removes pollutants, sediments, and contaminants. This helps to reduce the amount of pollutants entering natural water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and streams, and protects the quality of our water resources.
Furthermore, permeable pavements contribute to temperature moderation in urban areas. Traditional impervious pavement absorbs and radiates heat, leading to the formation of urban heat islands, which are areas with significantly higher temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas. Permeable pavements, on the other hand, allow rainwater to cool the surface and promote evaporation, reducing heat buildup and creating a more comfortable and pleasant outdoor environment.
Types of Permeable Paving Materials
There are various types of permeable paving materials available for sustainable landscapes. These materials include permeable interlocking concrete pavers, pervious concrete, porous asphalt, and gravel or crushed stone.
Permeable interlocking concrete pavers are a popular choice for driveways, patios, and walkways. These pavers are designed with spacing between them, allowing water to infiltrate into the ground. The gaps between the pavers can be filled with gravel or sand to enhance water permeability.
Pervious concrete is a porous material made by reducing the amount of sand and increasing the amount of coarse aggregate in the mix. Pervious concrete allows for water infiltration while providing a stable and durable surface for vehicular and pedestrian traffic. It is suitable for parking lots, sidewalks, and other areas with moderate to heavy loads.
Porous asphalt is similar to traditional asphalt but contains larger stone aggregates, which create void spaces for water infiltration. This type of paving material is commonly used for roads, parking lots, and driveways.
Gravel or crushed stone is a natural permeable material that can be used for various applications, such as walkways, patios, and driveways. These materials allow water to infiltrate into the ground and provide a rustic and aesthetically pleasing surface.
By using permeable paving materials in sustainable landscapes, we can manage stormwater runoff, improve water quality, and create environmentally friendly outdoor spaces that are both functional and visually appealing.
8. Rainwater Harvesting Techniques
Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable practice that involves collecting, storing, and using rainwater for various purposes, including irrigation, landscaping, and non-potable water needs. By capturing and utilizing rainwater, we can reduce the demand for freshwater sources, conserve water, and reduce stormwater runoff.
Rain Barrels
Rain barrels are a simple and cost-effective rainwater harvesting technique for sustainable landscapes. These barrels are connected to downspouts, which collect rainwater from rooftops during rainfall events. The rainwater is then stored in the barrels for later use in irrigation or non-potable water needs.
Rain barrels are available in various sizes and designs to suit different needs and preferences. They typically come with a screen or lid to prevent debris and mosquitoes from entering the barrel. A spigot at the bottom allows for easy access to the stored water, which can be used to water plants, wash outdoor equipment, or fill watering cans.
Rain barrels are an excellent way to conserve water, especially during dry periods or water restrictions. They provide a sustainable water source for gardens and landscapes, reduce the need for using treated drinking water for irrigation, and lower water bills.
Rain Gardens
Rain gardens are another effective rainwater harvesting technique for sustainable landscapes. A rain garden is a shallow depression in the ground that is designed to capture and absorb rainwater runoff. It is planted with a variety of native plants and grasses that can tolerate both wet and dry conditions.
During rainfall events, rainwater from roofs, driveways, or other hard surfaces is directed towards the rain garden. The depression allows the water to infiltrate into the soil, reducing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge. The plants in the rain garden help to absorb excess water, filter pollutants, and create habitat for wildlife.
Rain gardens offer several benefits in addition to rainwater harvesting. They help to prevent erosion, reduce flooding, and minimize pollution from stormwater runoff. Rain gardens also provide aesthetic value, attract birds and butterflies, and create a visually appealing and sustainable feature in the landscape.
By incorporating rainwater harvesting techniques, such as rain barrels and rain gardens, in sustainable landscapes, we can conserve water, reduce stormwater runoff, and create beautiful and resilient outdoor spaces that are well-adapted to local climatic conditions.
Challenges in Adopting Sustainable Landscapes
While sustainable landscapes offer numerous benefits, there are some challenges associated with their adoption. These challenges include initial costs and lack of awareness.
Initial Costs
One of the main challenges in adopting sustainable landscapes is the initial costs involved. Sustainable landscaping practices, such as installing solar-powered equipment, implementing efficient irrigation systems, or using permeable paving materials, may require a higher upfront investment compared to conventional practices. This can deter some homeowners or property owners from embracing sustainable landscaping.
However, it is important to consider the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits associated with sustainable landscapes. Many sustainable practices, such as water conservation, energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance needs, result in lower operational costs over time. By investing in sustainable landscaping practices, property owners can ultimately save money, reduce their ecological footprint, and create more resilient and valuable outdoor spaces.
Lack of Awareness
Another challenge in adopting sustainable landscapes is the lack of awareness and knowledge among homeowners, property owners, and landscaping professionals. Many people are not aware of the benefits of sustainable landscapes or the availability of zero emission tools and eco-friendly practices.
Education and outreach efforts are essential to increase awareness and promote the adoption of sustainable landscaping practices. Providing information on the environmental and economic benefits of sustainable landscapes, showcasing successful case studies, and offering training and resources to homeowners and landscaping professionals can help overcome the lack of awareness and drive the transition to more sustainable outdoor spaces.
How to Implement Sustainable Landscapes?
Implementing sustainable landscapes can be done in several steps. Whether you are starting from scratch or looking to improve an existing landscape, these steps can guide you through the process.
Steps to Get Started
-
Evaluate and Assess: Begin by evaluating your current landscape and identifying areas where sustainable practices can be implemented. Consider factors such as water use, energy consumption, waste generation, and plant selection.
-
Set Goals and Prioritize: Set specific goals for your sustainable landscape, such as reducing water consumption by 50% or eliminating the use of pesticides. Prioritize the areas that have the most significant environmental impact or offer the greatest potential for improvement.
-
Plan and Design: Develop a landscape plan and design that incorporates sustainable practices. Consider factors such as water-efficient irrigation systems, native and drought-tolerant plant selection, permeable paving solutions, and green waste management practices.
-
Select and Purchase Tools: Research and select zero emission tools that fit your specific needs and landscape requirements. Consider factors such as the size of your property, type of tasks, and available sunlight or electrical outlets. Purchase tools such as solar-powered equipment, electric machinery, or battery-powered tools.
-
Implement and Install: Begin implementing the sustainable practices identified in your plan. Install irrigation systems, plant native and drought-tolerant species, replace impervious pavement with permeable materials, and start composting or mulching green waste.
-
Educate and Maintain: Educate yourself and others about the benefits of sustainable landscapes and the proper use and maintenance of zero emission tools. Establish a routine maintenance schedule that includes efficient irrigation practices, proper pruning and mulching, and regular inspections of zero emission tools.
Getting Professional Assistance
If you are unsure about how to implement sustainable landscapes or require professional expertise, consider seeking assistance from landscape architects, environmental consultants, or sustainable landscaping experts. These professionals can provide guidance, technical expertise, and design services to help you achieve your sustainability goals.
Professional assistance can be particularly beneficial for larger or more complex projects, such as commercial landscapes or institutional settings. Landscape professionals can assess your site, develop a customized sustainable landscape plan, and oversee the implementation and maintenance process.
By getting professional assistance, you can ensure that your sustainable landscape is designed and managed effectively, maximizes resource conservation, and meets your specific needs and objectives.
Conclusion
Sustainable landscapes offer a holistic and eco-friendly approach to outdoor spaces. By adopting zero emission tools and sustainable practices, such as solar-powered equipment, electric machinery, efficient irrigation systems, green waste management, native plant selection, permeable paving, and rainwater harvesting, we can create landscapes that are beautiful, resilient, and environmentally responsible.
Incorporating sustainable practices in landscaping not only benefits the environment but also enhances the quality of life for users. Sustainable landscapes conserve water, reduce energy consumption, minimize pollution, support biodiversity, and create aesthetically pleasing and functional outdoor spaces.
While there may be challenges in adopting sustainable landscapes, such as initial costs and lack of awareness, the long-term benefits outweigh these challenges. By taking steps to implement sustainable practices and seeking professional assistance when needed, we can transform our outdoor spaces into models of sustainability and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. So, whether you are a homeowner, property owner, or landscaping professional, start making a difference today through sustainable landscapes made easy with zero emission tools at your service.