In this article, you will learn about the importance of zero-emission policies and how they are driving change for a greener tomorrow. We will discuss the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on the environment and the need for sustainable solutions. Additionally, we will explore the various initiatives and regulations being implemented worldwide to reduce emissions and promote cleaner technologies. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the role zero-emission policies play in creating a more sustainable future.

This image is property of www2.deloitte.com.
Zero-Emission Policies
Understanding Zero-Emission Policies
In today’s rapidly changing world, the need for sustainable solutions to combat climate change has never been more pressing. Zero-emission policies, also known as decarbonization strategies or green policies, are essential tools in creating a greener and cleaner future. These policies aim to reduce or eliminate greenhouse gas emissions from various sectors of the economy, such as transportation, energy production, and manufacturing.
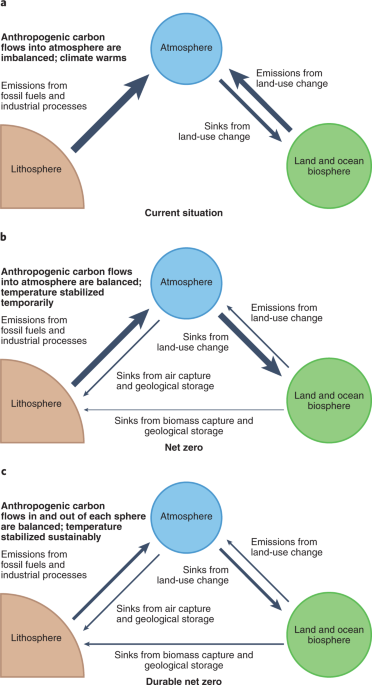
Zero-emission policies focus on transitioning away from fossil fuels and promoting the use of renewable energy sources. By implementing these policies, countries and cities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Importance of Zero-Emission Policies
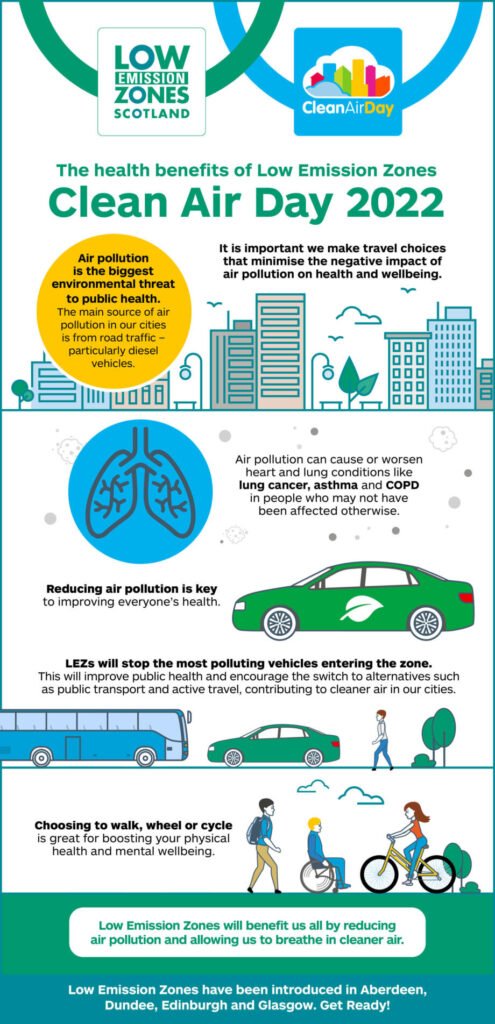
Zero-emission policies play a crucial role in addressing the climate crisis and achieving sustainability goals. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the main contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, a leading cause of global warming. By adopting zero-emission policies, nations can work towards reducing their emissions and limiting the adverse impacts of climate change.
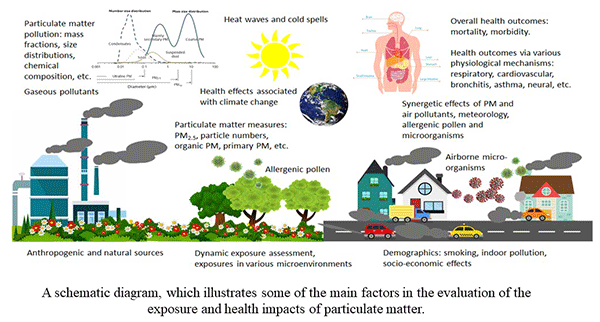
Moreover, zero-emission policies are essential for protecting public health and improving air quality. Fossil fuel combustion releases pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, which are harmful to human health and the environment. By transitioning towards cleaner energy sources, zero-emission policies can help decrease air pollution levels, leading to healthier communities.
Benefits of Zero-Emission Policies
Reducing Carbon Footprint
One of the primary benefits of zero-emission policies is their potential to significantly reduce carbon footprints. By shifting away from fossil fuels and adopting renewable energy sources, countries can reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change. This reduction in emissions is crucial in limiting the rise in global temperatures and avoiding the catastrophic consequences of a warming planet.
Improving Air Quality
Implementing zero-emission policies has a direct positive impact on air quality. Fossil fuel combustion for power generation and transportation releases pollutants that contribute to air pollution. By transitioning to cleaner sources of energy, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, zero-emission policies can help improve air quality, resulting in better health outcomes for communities and a reduced occurrence of respiratory diseases.
Promoting Renewable Energy
A key pillar of zero-emission policies is the promotion of renewable energy sources. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy, do not emit greenhouse gases during their operation. By incentivizing and supporting the development of renewable energy infrastructure, zero-emission policies can promote the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy systems.
Creating Green Jobs
Zero-emission policies create economic opportunities by fostering the growth of green industries. The shift towards renewable energy and sustainability requires skilled workers, such as engineers, technicians, and project managers. As countries invest in renewable energy projects and sustainable infrastructure, these policies can generate new jobs and an increased demand for skilled workers in the renewable energy sector.

This image is property of iea.imgix.net.
Implementation of Zero-Emission Policies
Setting Emission Reduction Targets
An essential aspect of implementing zero-emission policies is setting clear and ambitious emission reduction targets. By establishing targets, governments create a roadmap for action and provide a framework for measuring progress. These targets can be based on scientific evidence and aligned with international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius compared to pre-industrial levels.
Promoting Electric Vehicles
The transportation sector accounts for a significant portion of greenhouse gas emissions. To address this issue, zero-emission policies focus on promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) as an alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. By providing incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, governments can encourage consumers to transition to EVs, reducing emissions and improving air quality.
Investing in Sustainable Infrastructure
To support the transition to a zero-emission future, investments in sustainable infrastructure are crucial. Governments can allocate funds to develop renewable energy projects, such as wind and solar farms, and upgrade existing infrastructure to be more energy-efficient. Additionally, investments in public transportation systems, bike lanes, and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure can further reduce reliance on carbon-intensive transportation modes and encourage sustainable mobility options.
Challenges and Obstacles
Transitioning from Fossil Fuels
One of the main challenges in implementing zero-emission policies is the transition away from fossil fuels. As economies have historically relied on fossil fuels for energy production and transportation, shifting to alternative energy sources requires significant planning, investment, and infrastructure development. Overcoming the dependence on fossil fuels involves addressing complex political, economic, and technological challenges.
Costs and Affordability
Another obstacle to the widespread adoption of zero-emission policies is the perceived high costs of transitioning to cleaner energy sources and technologies. While renewable energy costs have significantly decreased in recent years, there may still be financial barriers for individuals and businesses to invest in renewable energy systems or electric vehicles. To overcome this challenge, governments can provide incentives, grants, and low-interest financing options to make renewable energy more affordable and accessible to all.
Resistance and Opposition
Resistance and opposition from various stakeholders, including fossil fuel industries and some political groups, can hinder the implementation of zero-emission policies. Some groups may argue that transitioning away from fossil fuels will result in job losses or economic instability. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, stakeholder engagement, and a clear demonstration of the economic opportunities and benefits associated with a transition to a low-carbon future.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Successful Case Studies
Sweden’s Fossil Fuel-Free Transportation
Sweden is a leading example of successful implementation of zero-emission policies. The country has set a target to become fossil fuel-free in the transportation sector by 2030. To achieve this, Sweden has heavily invested in electric vehicles, charging infrastructure, and renewable energy sources. As a result, electric vehicles have become increasingly popular, and charging stations are now readily available throughout the country.
California’s Zero-Emission Vehicle Program
California, a pioneer in environmental regulations, has implemented a Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector. Under this program, automakers must sell a certain percentage of zero-emission vehicles in the state. California’s ZEV program has incentivized the adoption of electric vehicles and has played a pivotal role in increasing EV market share in the state.
Effects on Various Sectors
Transportation Sector
Zero-emission policies have a significant impact on the transportation sector. By promoting the adoption of electric vehicles, investing in public transportation systems, and supporting active modes of transportation, such as walking and cycling, zero-emission policies aim to reduce emissions from transportation and improve overall mobility. Furthermore, the use of renewable fuels, such as biofuels and hydrogen, can also contribute to decarbonizing the aviation and shipping industries.
Energy Sector
Transitioning to zero-emission policies has profound implications for the energy sector. By promoting renewable energy sources, governments can reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based power generation and achieve a more sustainable energy mix. The integration of renewable energy into the grid can also create opportunities for decentralized energy production, such as rooftop solar panels, and enable communities to become more self-sufficient in meeting their energy needs.
Urban Planning and Development
Zero-emission policies influence urban planning and development practices by promoting sustainable and low-carbon cities. These policies encourage the development of energy-efficient buildings, the establishment of green spaces, and the creation of walking and cycling infrastructure. By designing cities with zero-emission goals in mind, governments can improve the quality of life for urban residents, reduce traffic congestion, and create more resilient and sustainable communities.
Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry plays a crucial role in the transition to a zero-emission future. By adopting cleaner production methods, implementing energy-efficient technologies, and reducing waste, manufacturers can significantly decrease their carbon footprint. Additionally, the production of renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can create new job opportunities and stimulate economic growth.

This image is property of vision.esa.int.
Global Cooperation and Collaboration
International Agreements and Accords
Global cooperation is essential for effectively addressing climate change and implementing zero-emission policies. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, provide a framework for countries to collaborate and set collective emission reduction targets. By participating in these agreements, countries can share best practices, exchange knowledge and technology, and work towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Sharing Best Practices
Sharing best practices among countries and cities is crucial for the successful implementation of zero-emission policies. By highlighting successful case studies and lessons learned, governments and policymakers can learn from each other’s experiences and accelerate the adoption of effective strategies. International conferences, workshops, and online platforms facilitate the sharing of best practices and foster collaboration on a global scale.
Supporting Developing Countries
Supporting developing countries in their efforts to implement zero-emission policies is essential for global sustainability. Developed nations can provide financial assistance, technology transfer, and capacity-building support to enable developing countries to transition to cleaner energy sources and adopt sustainable practices. By ensuring a just and inclusive transition, we can address global inequality and build a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Public Awareness and Education
Educating the Masses
Public awareness and education play a crucial role in driving the adoption of zero-emission policies. Governments, educational institutions, and non-profit organizations can implement educational campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of reducing emissions, the benefits of renewable energy, and the role individuals can play in mitigating climate change. By empowering individuals with knowledge, we can cultivate a sense of responsibility and encourage collective action.
Media and Information Dissemination
The media plays a critical role in disseminating information about zero-emission policies and climate change. Media outlets can provide accurate and balanced reporting on environmental issues, highlight success stories, and debunk myths and misconceptions surrounding renewable energy. By engaging with the media, governments and organizations can ensure that accurate information reaches the public and fosters informed decision-making.
Promoting Sustainable Lifestyles
Zero-emission policies go beyond institutional actions; they require a shift towards sustainable lifestyles. Individuals can contribute to the transition to a zero-emission future by adopting energy-efficient practices, reducing waste, and choosing sustainable modes of transportation. Governments and organizations can support these individual efforts by providing incentives, educational resources, and infrastructure that enables sustainable living.

This image is property of thesciencesurvey.com.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in Renewable Energy
Technological advancements in renewable energy have played a crucial role in the success of zero-emission policies. The development of more efficient solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems has made renewable energy more cost-effective and accessible. Continued research and development in renewable energy technologies hold the promise of further reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and expanding the deployment of clean energy solutions.
Battery and Storage Solutions
Battery and storage technologies are essential components of zero-emission policies. Energy storage systems enable the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid and provide a reliable and flexible energy supply. Advancements in battery technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, have made electric vehicles more practical and affordable, further driving the transition towards zero-emission transportation.
Smart Grid Systems
Smart grid systems play a crucial role in enabling the widespread adoption of renewable energy and efficient energy management. These advanced electrical grids incorporate digital technologies and real-time data to optimize energy distribution, monitor energy consumption, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. Smart grid systems promote energy efficiency, reduce energy wastage, and support the decarbonization of the energy sector.
Economic Opportunities
Green Investments and Businesses
Zero-emission policies create economic opportunities by driving investments in green industries. As governments and businesses transition to cleaner energy sources, there is a growing demand for renewable energy infrastructure, energy-efficient technologies, and sustainable products and services. This shift towards a low-carbon economy can stimulate economic growth, attract investment, and create jobs in sectors such as renewable energy generation, sustainable agriculture, and green transportation.
Job Creation in the Renewable Energy Sector
The widespread adoption of zero-emission policies leads to job creation in the renewable energy sector. The transition to renewable energy requires skilled professionals, such as engineers, technicians, and project managers, who can design, install, and maintain renewable energy systems. These jobs provide stable employment opportunities and support local economies, particularly in regions where traditional fossil fuel industries may decline.
Government Incentives and Regulations
Tax Breaks and Incentives
Governments can provide tax breaks and incentives to encourage individuals and businesses to adopt zero-emission technologies and practices. Tax credits for purchasing electric vehicles, installing solar panels, or implementing energy-efficient measures can offset the initial costs and make these sustainable options more attractive. By rewarding sustainable choices with financial incentives, governments can accelerate the adoption of zero-emission solutions.
Mandates and Regulations
Mandates and regulations are essential tools in driving the adoption of zero-emission policies. Governments can establish targets and regulations that require a certain percentage of energy to come from renewable sources, incentivize the implementation of energy efficiency measures, or promote the use of electric vehicles. These policies create a level playing field and provide clear guidelines for businesses and individuals to transition towards zero-emission solutions.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
To ensure the effectiveness of zero-emission policies, governments can establish penalties for non-compliance. By imposing fines or penalties on organizations or individuals that fail to meet emission reduction targets or fail to adopt sustainable practices, governments create a strong incentive for compliance and promote accountability. Penalties for non-compliance serve as a deterrent and encourage businesses and individuals to take their environmental responsibilities seriously.
Public-Private Partnerships
Collaboration between Governments and Corporations
Public-private partnerships are crucial in driving the implementation of zero-emission policies. Collaboration between governments and corporations enables the pooling of resources, expertise, and innovation to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy. Government regulations and incentives can provide a supportive framework, while businesses can contribute through investments, technological advancements, and sustainable practices.
Investment and Funding Opportunities
Zero-emission policies create investment and funding opportunities in various sectors. Governments can attract private sector investments by offering incentives and guarantees for infrastructure projects, renewable energy installations, and research and development initiatives. In turn, private investors can contribute much-needed capital and expertise to support the implementation of zero-emission policies, fostering a mutually beneficial partnership for both parties.
Overcoming Resistance and Skepticism
Addressing Disinformation and Misconceptions
Resistance and skepticism towards zero-emission policies often stem from misinformation and misconceptions about renewable energy and climate change. Addressing disinformation requires effective communication strategies that provide accurate and accessible information to the public. Governments, educational institutions, and scientists play a crucial role in dispelling myths and engaging in public dialogue to address concerns and foster understanding.
Engaging with Stakeholders
Engaging with stakeholders is essential in addressing resistance to zero-emission policies. Governments and organizations can actively involve citizens, communities, and industries in the decision-making process, ensuring that diverse perspectives are heard and valued. Collaboration with stakeholders fosters ownership, builds trust, and increases the chances of successful policy implementation.
Fostering Dialogue
Fostering dialogue and open discussions about zero-emission policies contribute to overcoming resistance and skepticism. By creating platforms for dialogue, governments can facilitate meaningful conversations between policymakers, scientists, businesses, and citizens. These discussions allow for the exchange of ideas, concerns, and solutions, enabling a collective understanding of the benefits and challenges associated with transitioning to a zero-emission future.
Conclusion
The Path to a Sustainable Future
Zero-emission policies are crucial in driving the necessary changes to address climate change and create a sustainable future. By adopting these policies, countries and cities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, improve air quality, and promote the use of renewable energy sources. The implementation of zero-emission policies requires a collective effort involving governments, businesses, and individuals to transition towards a low-carbon economy.
Collective Responsibility for Change
Addressing the challenges of climate change and achieving sustainability goals is a collective responsibility. Governments must take the lead in implementing zero-emission policies by setting ambitious targets, creating supportive regulations, and providing incentives for sustainable practices. At the same time, businesses, communities, and individuals must actively participate by adopting sustainable lifestyles, supporting renewable energy, and engaging in sustainable initiatives. Together, we can drive change for a greener tomorrow and create a sustainable future for generations to come.