is an article that discusses the importance of adopting a sustainable approach to landscaping for a greener environment. Throughout the article, you will learn about the various benefits of zero-emission landscaping, including reduced carbon footprint, improved air and water quality, and increased biodiversity. You will also discover practical tips and techniques for implementing zero-emission landscaping practices in your own outdoor spaces. By the end of the article, you will have a better understanding of how to create beautiful and environmentally-friendly landscapes that contribute to a healthier planet.
This image is property of www.europenowjournal.org.
Introduction
Welcome to the world of Zero Emission Landscaping, where sustainability and environmental consciousness meet. In an era of increasing concern about climate change and the depletion of natural resources, adopting sustainable practices in landscaping has become more important than ever. Zero Emission Landscaping offers a holistic approach that not only beautifies outdoor spaces but also minimizes environmental impact and promotes biodiversity. In this article, we will explore the importance of Zero Emission Landscaping, the principles and techniques involved, successful case studies, challenges, and the measurable environmental impact it can make. So, let’s embark on this green journey together!
Benefits of Green Spaces
Before diving into the details of Zero Emission Landscaping, let’s first acknowledge the importance of green spaces in our lives. Green spaces, such as parks, gardens, and even office landscapes, offer numerous benefits to individuals and communities.
First and foremost, green spaces provide a sanctuary from the hustle and bustle of urban life. They offer a place for relaxation, recreation, and social interaction. Spending time in nature has been proven to reduce stress, improve mental health, and enhance overall well-being.
Moreover, green spaces play a vital role in mitigating the effects of climate change. Trees, for example, absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. They also provide shade, reducing the need for artificial cooling and consequently lowering energy consumption.
Green spaces also act as natural filters by capturing pollutants from the air, improving air quality. They help reduce the urban heat island effect, where cities tend to be significantly hotter than their rural counterparts due to the abundance of concrete and lack of vegetation.
Lastly, green spaces provide habitats for various plant and animal species, supporting biodiversity. They create ecological corridors and allow the movement of wildlife, promoting a healthy and balanced ecosystem.

This image is property of lawnlove.com.
Environmental Impact of Traditional Landscaping Practices
Unfortunately, traditional landscaping practices have not always been environmentally friendly. Conventional methods often involve excessive use of water, chemical pesticides, and herbicides, and the depletion of natural resources. These practices contribute to pollution, water scarcity, soil degradation, and loss of biodiversity.
For instance, irrigating landscapes accounts for a substantial amount of water consumption in many regions. Inefficient watering systems, such as overhead sprinklers, result in water waste through evaporation and runoff. Furthermore, the use of chemical pesticides and herbicides not only harms beneficial insects and wildlife but also pollutes soil and water sources.
Additionally, the extensive use of non-native and high-maintenance plants in traditional landscaping requires more resources and energy to maintain. These plants often require frequent watering, fertilizing, and pruning, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions and further straining natural resources.
Transition to Sustainable Landscaping
Recognizing the negative environmental impact of traditional landscaping practices, there has been a growing movement towards sustainable landscaping approaches. Zero Emission Landscaping is one such approach that aims to minimize or eliminate the use of polluting resources and practices.
By adopting sustainable principles and techniques, it is possible to create landscapes that benefit both individuals and the environment. Zero Emission Landscaping focuses on using native plants, reducing water consumption, implementing organic practices, avoiding chemical pesticides and herbicides, and encouraging biodiversity.
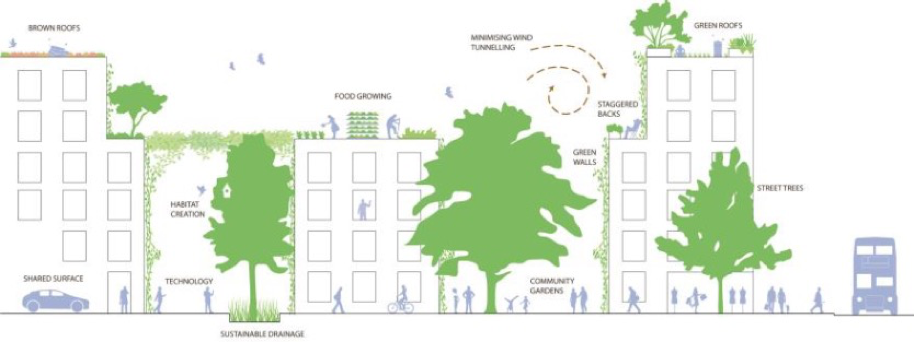
This image is property of www.europenowjournal.org.
Principles of Zero Emission Landscaping
Using Native Plants
One of the fundamental principles of Zero Emission Landscaping is the use of native plants. These are plants that naturally occur in a specific region and have adapted to its climate, soil conditions, and wildlife interactions. By planting native species, you are creating a self-sustaining ecosystem that requires minimal maintenance and resources.
Reducing Water Consumption
Water conservation is a critical aspect of Zero Emission Landscaping. By implementing water-efficient practices, such as xeriscaping, drip irrigation, and rainwater harvesting, you can reduce water consumption significantly. Xeriscaping involves selecting drought-tolerant plants, using mulch to retain moisture, and designing landscapes that minimize water runoff.
Implementing Organic Practices
Organic practices involve using natural methods to maintain healthy soil and plants without the need for chemical fertilizers, pesticides, or herbicides. Composting, for example, allows you to create nutrient-rich soil amendments from organic waste. Natural pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or using companion planting techniques, can help manage pests without resorting to harmful chemicals.
Avoiding Chemical Pesticides and Herbicides
Chemical pesticides and herbicides have adverse effects on the environment, wildlife, and human health. In Zero Emission Landscaping, these harmful substances are avoided altogether. Instead, alternative methods, such as hand weeding and mechanical weed control, are employed to manage unwanted vegetation.
Encouraging Biodiversity
Biodiversity is essential for a healthy and resilient ecosystem. By incorporating a variety of plant species, you can attract different pollinators, birds, and other wildlife. Including features like bird feeders, bat houses, and butterfly gardens can further enhance biodiversity in your landscape.
Native Plants for Zero Emission Landscaping
Benefits of Using Native Plants
Using native plants in your landscape offers numerous benefits. Firstly, native plants are well adapted to the local climate, making them more resilient to droughts, temperature extremes, and pests. They require less water, fertilizer, and pesticides compared to non-native species.
Furthermore, native plants provide crucial food and shelter for local wildlife. By planting native flowering plants, you can attract bees, butterflies, and birds, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
Choosing the Right Native Plants for Different Regions
When selecting native plants for your landscape, it is important to choose species that are well-suited to your specific region’s climate and soil conditions. Consulting local resources such as native plant nurseries or botanical gardens can help you identify the most suitable plants for your area.
Creating Habitat for Local Wildlife
By incorporating native plants in your landscape design, you are creating valuable habitat for local wildlife. Consider including features such as bird baths, butterfly host plants, and nesting boxes to attract and support a diversity of species. Providing a water source and sheltered areas will encourage wildlife to make your landscape their home.

This image is property of www.europenowjournal.org.
Water Conservation Techniques
Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping is a water-efficient landscaping technique that focuses on selecting plants and designing landscapes that require minimal irrigation. It involves using drought-tolerant plants, efficient watering methods, and mulching to conserve water. Xeriscaping not only reduces water consumption but also saves time, money, and energy associated with landscape maintenance.
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a precise and efficient watering method that delivers water directly to the plant’s root zone. It minimizes water waste by reducing evaporation and runoff. By using drip irrigation systems, you can ensure that water is delivered where it is needed most, resulting in healthier plants and lower water bills.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater for later use in irrigation. This technique utilizes rain barrels, cisterns, or underground storage systems to capture and store rainwater runoff from roofs and paved surfaces. By harvesting rainwater, you can reduce reliance on municipal water sources and contribute to water conservation efforts.
Mulching
Mulching is a simple yet effective technique that involves covering the soil surface with organic or inorganic materials, such as wood chips, straw, or gravel. Mulch helps retain soil moisture, prevent weed growth, regulate soil temperature, and improve overall soil health. By mulching your landscape beds, you can reduce water evaporation and minimize the need for frequent watering.
Organic Practices in Landscaping
Composting
Composting is the process of decomposing organic material into nutrient-rich soil amendments. It involves collecting organic waste, such as leaves, grass clippings, and kitchen scraps, and allowing them to break down naturally over time. Compost improves soil structure, promotes healthy plant growth, and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Natural Pest Control
Rather than relying on chemical pesticides, Zero Emission Landscaping encourages natural pest control methods. This includes introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs or praying mantises, that feed on pests. Companion planting, where different plant species are grown together to deter pests, is another effective strategy.
Soil Management
Maintaining healthy soil is crucial for a thriving landscape. Zero Emission Landscaping emphasizes soil testing to determine its nutrient composition and pH levels. Based on the test results, organic soil amendments, such as compost or natural minerals, can be added to improve soil fertility and structure.
Using Organic Fertilizers
In place of synthetic fertilizers, organic fertilizers derived from natural sources, such as compost, bone meal, or fish emulsion, are used. Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, preventing nutrient runoff and promoting long-term soil health. These fertilizers improve plant growth and minimize the risk of chemical pollution in water sources.
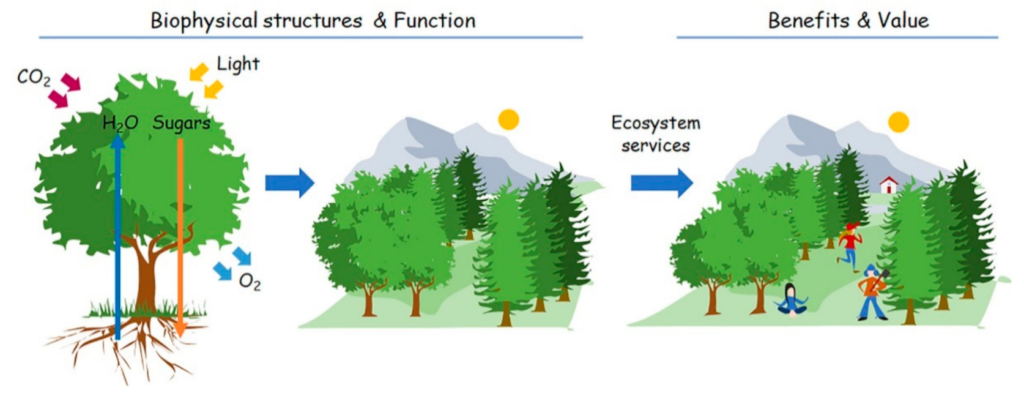
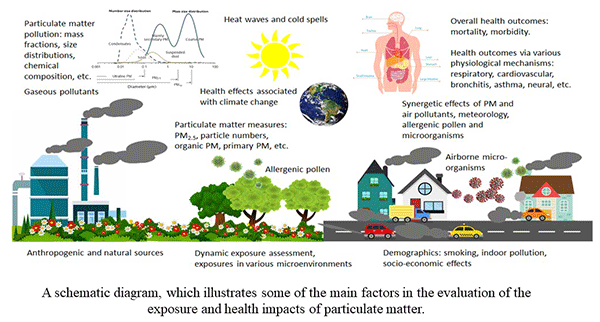
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Green Infrastructure in Landscaping
Benefits of Green Roofs
Green roofs, also known as vegetated roofs or living roofs, offer multiple benefits for both buildings and the environment. By installing plants on rooftops, green roofs help reduce stormwater runoff, regulate building temperatures, extend roof lifespan, improve air quality, and create habitat for birds and insects. They also add aesthetic value to urban landscapes.
Installing Permeable Pavements
Traditional pavement materials, such as concrete or asphalt, often contribute to urban runoff and water pollution. Permeable pavements, on the other hand, allow water to soak into the ground, reducing stormwater runoff and recharging groundwater. These pavements can be made from porous materials or include gaps for vegetation growth, such as grass pavers.
Rain Gardens
Rain gardens are landscaped areas specifically designed to capture and absorb rainwater runoff from roofs, driveways, and other impervious surfaces. By directing water towards these depressions, rain gardens can reduce stormwater runoff and promote groundwater recharge. They also provide attractive, low-maintenance planting opportunities and can be tailored to attract pollinators.
Living Walls
Living walls, also known as green walls or vertical gardens, are vertical structures covered in plants. They can be either freestanding or attached to existing walls or buildings. Living walls provide insulation, improve air quality, reduce noise, and create a visually stunning display of plant life. They are an excellent solution for maximizing green space in urban environments.
Renewable Energy in Landscaping
Solar-Powered Lighting
Incorporating solar-powered lighting into landscapes provides an eco-friendly alternative to traditional lighting. Solar lights harness energy from the sun during the day and store it in batteries to be used for illumination at night. By relying on renewable energy, solar-powered lighting reduces carbon emissions and eliminates the need for electrical outlets or wiring.
Wind Energy for Water Features
Water features, such as fountains or waterfalls, can be powered by wind turbines to reduce their environmental impact. Wind energy is a clean and renewable source of power that can be harnessed on-site to create a more sustainable and self-sufficient landscape.
Use of Electric Equipment
Zero Emission Landscaping promotes the use of electric equipment instead of gas-powered machinery. Electric tools, such as lawnmowers, leaf blowers, and trimmers, are quieter, produce no emissions, and require less maintenance. With the increasing availability and advancements in battery technology, electric equipment is becoming a viable and environmentally friendly choice.
Education and Awareness for Zero Emission Landscaping
Training for Landscapers and Gardeners
To promote the adoption of Zero Emission Landscaping practices, it is essential to provide training and education to industry professionals such as landscapers and gardeners. Workshops, seminars, and certifications can equip them with the necessary knowledge and skills to implement sustainable techniques.
Community Outreach Programs
Engaging with the local community through outreach programs can create awareness and encourage participation in Zero Emission Landscaping initiatives. Public workshops, guided tours, and volunteer opportunities in community gardens are effective ways to educate and inspire individuals to embrace sustainable landscaping practices.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a significant role in promoting the benefits of Zero Emission Landscaping and encouraging behavior change. By leveraging social media, websites, and traditional advertising channels, these campaigns can reach a broader audience and inspire individuals to take action in their own landscapes.
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Involvement of Local Government
The involvement of local government is crucial for promoting Zero Emission Landscaping on a broader scale. Governments can introduce incentives such as tax breaks or rebates for adopting sustainable landscaping practices. They can also enforce regulations that limit the use of harmful chemicals, encourage native plantings, or require water-efficient irrigation systems.
Partnerships with Environmental Organizations
Collaborating with environmental organizations can provide valuable resources and expertise. These organizations often have access to research, funding opportunities, and community networks that can support Zero Emission Landscaping initiatives. By working together, stakeholders can create a more significant impact and drive positive change.
Engagement with Property Owners
Engaging property owners in the transition to Zero Emission Landscaping is crucial. Homeowners, businesses, and organizations can be encouraged to embrace sustainable practices through educational materials, financial incentives, or professional counseling. By demonstrating the long-term benefits and cost savings associated with sustainable landscaping, property owners are more likely to make the switch.
Cost Considerations in Zero Emission Landscaping
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
Adopting Zero Emission Landscaping practices may require an initial investment, but the long-term savings are substantial. Water-efficient irrigation systems, reduced maintenance costs, and lower energy bills from using renewable energy can offset the initial expenses. Moreover, the increased property value, improved aesthetics, and environmental benefits contribute to a more sustainable and desirable landscape.
Economic Incentives for Sustainable Practices
To motivate individuals and organizations to embrace Zero Emission Landscaping, there are various economic incentives available. These can include tax credits, rebates, or grants specifically aimed at sustainable landscaping projects. Governments, utility companies, or environmental organizations often offer these incentives to promote environmentally friendly practices.
Case Studies of Successful Zero Emission Landscaping Projects
Urban Parks
Urban parks provide excellent opportunities for Zero Emission Landscaping. Central Park in New York City, for example, has implemented sustainable practices such as using compost for soil amendment, reducing water consumption through efficient irrigation, and incorporating native plant species. These initiatives have resulted in improved biodiversity, reduced ecological footprint, and enhanced visitor experience.
Residential Gardens
Many homeowners have embraced Zero Emission Landscaping in their own gardens. By using native plants, incorporating water-saving techniques, and employing organic practices, residential gardens can become thriving ecosystems. These landscapes not only promote biodiversity but also inspire neighbors and passersby to adopt similar practices.
Corporate Campuses
Corporate campuses have the potential to make a significant impact by adopting Zero Emission Landscaping principles. Google’s headquarters, for example, features extensive green roofs, rain gardens, and native plantings. These initiatives have not only reduced the ecological footprint but also created aesthetically pleasing and employee-friendly outdoor spaces.
Challenges and Solutions for Zero Emission Landscaping
Limited Availability of Native Plants
One of the challenges in Zero Emission Landscaping is the limited availability of native plant species. Nurseries and garden centers often stock a limited selection of plants, making it challenging to source a diverse range of native species. However, with increased demand and awareness, nurseries are beginning to expand their offerings and promote the use of native plants.
Managing Pests and Diseases Without Chemicals
Pest and disease management without the use of chemicals can be a challenge for Zero Emission Landscaping. However, alternative methods, such as biological controls or cultural practices, can effectively manage pests and diseases. Regular monitoring, proper plant selection, and good cultural practices, such as appropriate watering and fertility management, can help prevent outbreaks and promote plant health.
Educating Clients About the Benefits
Another challenge is educating clients about the benefits of Zero Emission Landscaping and overcoming any hesitations or misconceptions they may have. Providing case studies, testimonials, and demonstrations of successful projects can help overcome resistance and showcase the long-term advantages, such as lower maintenance costs and a healthier environment.
Overcoming Budget Constraints
Budget constraints can be a significant roadblock in implementing Zero Emission Landscaping. Sustainable practices may require upfront investment, and clients or property owners might be hesitant due to financial concerns. However, by highlighting the long-term savings, economic incentives, and the positive environmental impact, it is possible to overcome these constraints and demonstrate the value of sustainable landscapes.
Measuring the Environmental Impact
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Zero Emission Landscaping significantly contributes to carbon footprint reduction. The use of renewable energy, such as solar-powered lighting or wind energy, mitigates the use of fossil fuels. Planting native trees and vegetation sequesters carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, further reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Air and Water Quality Improvement
By avoiding chemical pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, Zero Emission Landscaping improves air and water quality. It minimizes the introduction of harmful substances into the environment, reducing pollution and promoting a healthier ecosystem. Water conservation techniques, such as rainwater harvesting and proper irrigation practices, also help reduce water pollution and protect local water sources.
Biodiversity Monitoring
Zero Emission Landscaping actively promotes biodiversity through the use of native plants and habitat creation. Monitoring biodiversity within these landscapes can provide valuable insights into the success of conservation efforts. Observing changes in the population of flora and fauna, monitoring the presence of bird species, or tracking insect diversity are some ways to measure the impact on biodiversity.
Conclusion
Zero Emission Landscaping offers a sustainable approach to creating greener spaces that benefit both individuals and the environment. By adopting principles such as using native plants, reducing water consumption, implementing organic practices, and incorporating green infrastructure and renewable energy, landscapes can become hubs of biodiversity and contribute to a healthier planet. Although challenges exist, such as limited availability of native plants and educating clients, the long-term benefits, cost savings, and measurable environmental impact make the transition to Zero Emission Landscaping worth it. So why wait? Start transforming your landscape today and be a part of this sustainable movement towards greener spaces!